Cross-Platform
Cross-platform software is software that is available for more than one computer platform. Each version of a cross-platform application may have slight differences in the user interface and feature set, but they are fundamentally the same program capable of opening the same files and performing the same functions. The opposite of a cross-platform app is a "native" app, developed exclusively for a single platform.
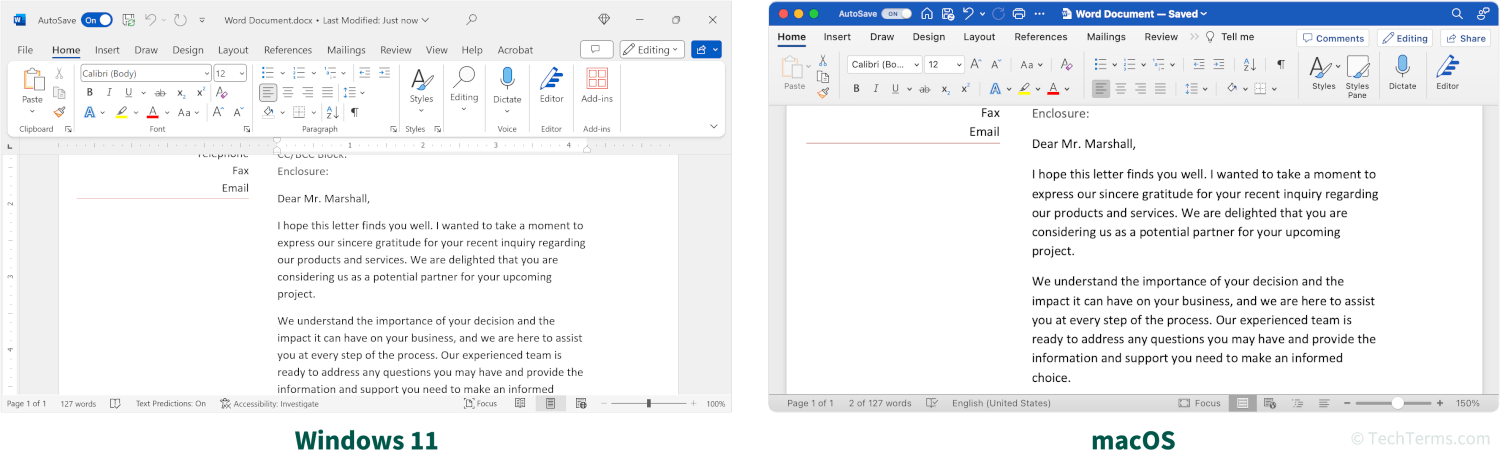
Some cross-platform apps are available for both desktop and mobile platforms. In these cases, the mobile version of the app may have a limited feature set, but is compatible with the same documents and capable of most of its functions. For example, Microsoft Word is a cross-platform app with a full-featured desktop version available for Windows and macOS; it also offers a mobile version for iOS and Android and a web app that can run in a browser.
Historically, each version of a cross-platform application required separate source code using each platform's native programming languages and APIs. However, modern cross-platform app frameworks and libraries help developers create apps using a single code base capable of running on multiple platforms. For example, the Electron app framework uses web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to allow apps to run on desktop and mobile platforms.
NOTE: Hardware peripherals compatible with multiple platforms, like USB mice and keyboards, may also be considered cross-platform.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge