Pipeline
A pipeline in the context of computer processing is a technique for executing multiple instructions at once. Computer processors can handle millions of instructions per second. Every instruction goes through several stages, each processed by a different part of the processor. With each clock cycle, an instruction moves from one stage to the next, and while one instruction is going through one stage, other instructions are simultaneously going through different stages.
A typical CPU pipeline involves five stages — instruction fetch, instruction decode, execute, memory access, and write back (although this may vary by architecture). Without pipelining, a processor could handle only one instruction at a time. Since it takes several clock cycles for each instruction to move through all the stages, most of the processor would sit idle while a single instruction moves from stage to stage. Non-pipelined processing does not make a single instruction take longer, but it does mean that the processor can process fewer instructions per second.
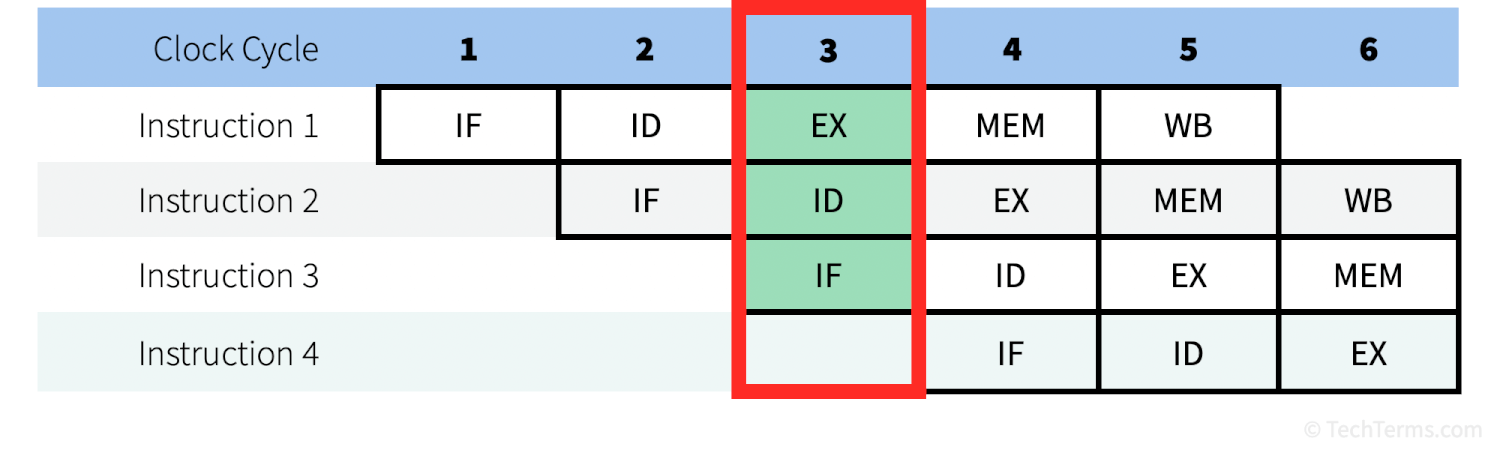
Instruction pipelining works a lot like an automotive assembly line, where each station has a single task — installing seats, mounting the engine, attaching the wheels, etc. If only one car is moving down the line at a time, most of those stations are sitting idle, and the factory won't be able to make many cars in a day. However, if dozens of vehicles are on the line at once — enough to keep each station busy — far more cars will be completed in a single day even though each one still takes the same time.
GPU Graphics Pipelines
In addition to CPUs, computer GPUs also use pipelining to process instructions. The GPU graphics pipeline is more complex, involving several dedicated processing components that perform mathematical functions to render 3D scenes and objects into 2D images displayed on a screen.
GPU architectures vary significantly from generation to generation, but most graphics pipelines follow a similar pattern. A simple graphics pipeline starts by converting the 3D coordinates of vertices (the corners of the triangles that make up every 3D object) into 2D coordinates on the flat plane of a screen. It turns those coordinates into wireframes, then fills in the geometry between those vertices to create shapes. Next, it rasterizes those shapes into pixels by adding texture maps, lighting, and other shader effects. Hidden pixels and other information not visible to the "camera" are discarded, then the final image is saved to the frame buffer and displayed on the screen.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge