Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt is a high-speed I/O interface developed by Intel and Apple. It is based on the PCI Express and DisplayPort technologies and supports both data devices and displays. The first two generations of Thunderbolt use the Mini DisplayPort connector, while the third and fourth generations use a USB-C connector.
Since Thunderbolt is based on the PCI Express architecture, external devices connected via Thunderbolt can achieve performance that was previously only possible from internal components. The first-generation Thunderbolt interface offered 10 Gpbs of throughput in both directions, later improving to 40 Gbps in third- and fourth-generation connections — 8 times the bandwidth of USB 3.0 and 4 times that of USB 3.1.
Like USB and FireWire, Thunderbolt can provide power to connected peripheral devices — up to 10 watts for first- and second-generation connections or up to 100 watts for third- and fourth-generation Thunderbolt. That means external devices, like monitors and external storage devices, can draw their power directly from the Thunderbolt port. Additionally, simple adapters can connect USB, FireWire, and Ethernet devices to a Thunderbolt port.
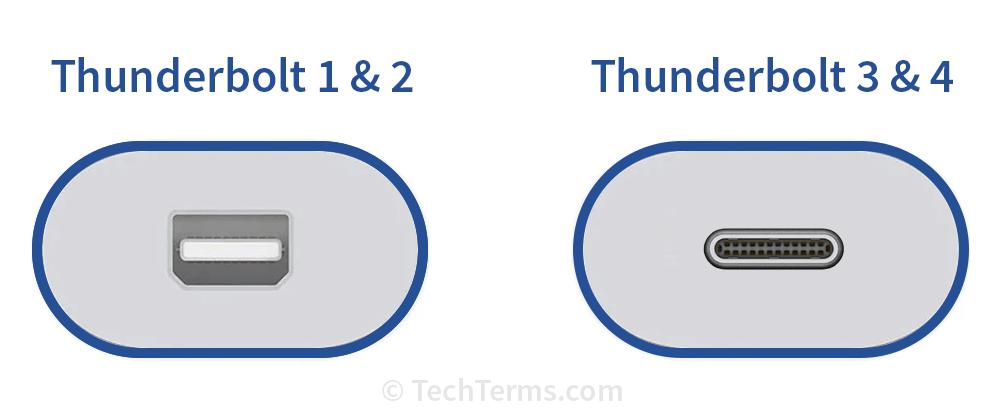
While Thunderbolt is primarily used as a high-speed data interface, it can also be used to connect to high-resolution displays. The first- and second-generation Thunderbolt interface is physically identical to the Mini-DisplayPort interface and therefore can be used to connect a DisplayPort monitor. The third- and fourth-generation Thunderbolt interface sends DisplayPort data over a USB-C connector instead, which is less common but supported by some monitors. Like HDMI, DisplayPort supports both audio and video, eliminating the need for a separate audio cable.
Thunderbolt devices can be daisy-chained, meaning multiple devices can connect in sequence to a single Thunderbolt port. For example, you can connect a Thunderbolt display to a computer and a Thunderbolt external hard drive to the display. You could also connect a second Thunderbolt monitor to the first display. This means you can connect two external displays to a laptop, as long as the laptop supports the resolution required for two screens.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge