USB
Stands for "Universal Serial Bus." USB is the most common type of port found on modern computers. It is used to connect various peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, game controllers, printers, scanners, and external storage devices.
USB provides both data transmission and low voltage (5V) power over a single cable. Devices that require five volts or less can operate over USB without an external power source. A single USB bus supports up to 127 devices, using multiple USB hubs.
USB has gone through many evolutions since its introduction in 1997. There are now several different versions and different types of USB connectors:
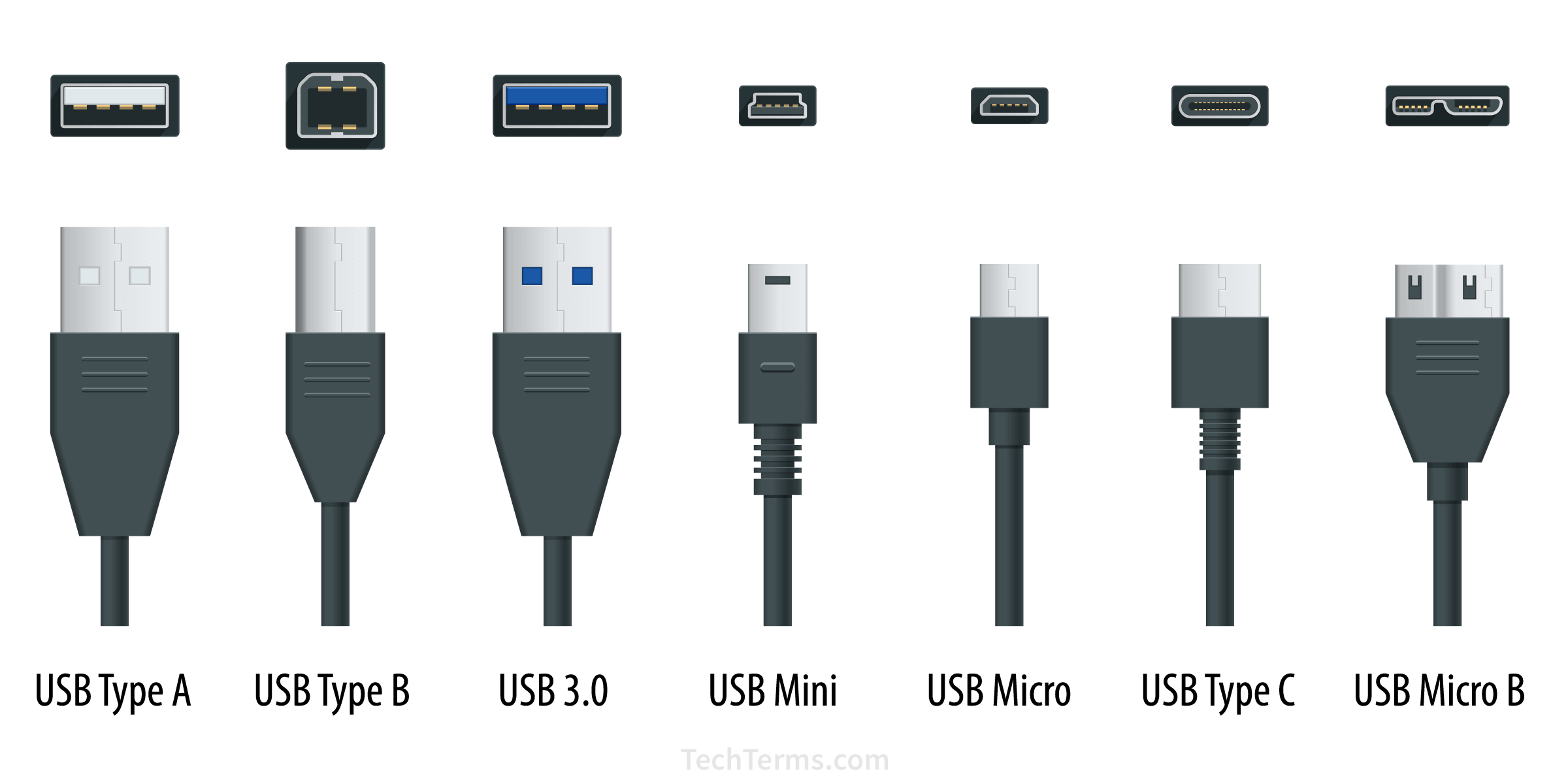
Below are different USB standards and their corresponding ports and maximum data transfer rates. The port colors listed below are common but are not required and may differ between manufacturers.
- USB 1.0 (white USB-A and USB-B — very rare) → 1.5 Mbps
- USB 1.1 (white USB-A and USB-B, Mini-USB) → 12 Mbps
- USB 2.0 (black USB-A and USB-B, Mini-USB, Micro-USB) → 480 Mbps
- USB 3.0 / SuperSpeed (blue USB-A and USB-B, Micro-USB B) → 5 Gbps
- USB 3.1 / SuperSpeed+ (green USB-A and USB-B, USB Type C) → 10 Gbps
- USB 3.2 (USB Type C) → 20 Gbps
- USB 4 (USB Type C) → 40 Gbps
Since USB devices, ports, and cables all use the same underlying USB communications standard, they are often compatible with physical adapters. However, when combining USB standards, the data transfer speed is limited to the lowest standard in the connection.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge