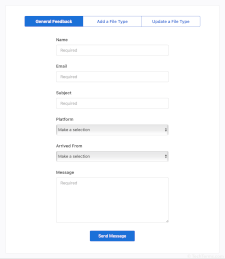
Form
A form is a user interface element within a website or software application that allows you to enter and submit data. It contains one or more fields and an action button, such as Save or Submit.
Web Forms
Web forms allow you to submit information to a website via a web browser. Examples include registration forms, online surveys, and contact forms. When you click , the web server hosting the website processes the data you entered in the form. For example, a feedback form may send an email to the webmaster. A registration form may create a new account in a database.
A web form is a standard HTML element, created using the <form> tag. Elements within a form may include:
- <input type="text"> – a one-line text input field for name, email address, etc.
- <textarea> – a large text field that supports multiple lines of text; often used for messages
- <select> – a dropdown menu with multiple options, defined by <option> tags
- <input type="hidden"> – a hidden field used to submit additional data, such as a timestamp or referring page URL
- <input type="submit"> – a button used for submitting the data entered in the form.
NOTE: Form data is often processed by a server-side script, but form validation (such as verifying required fields) is usually performed by client-side JavaScript or HTML checks.
Application Forms
While forms are commonly associated with websites, many software programs also include forms. For instance, database applications allow you to create custom forms to enter data more quickly. Media converters provide forms that enable you to choose audio and video compression settings. All dialog boxes, such as Print and Save As windows, are considered forms because they include selectable options and a primary action button.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge