Socket
A socket is a software component that helps computer programs communicate over a network. The term "socket" evokes a physical socket that you plug a networking cable into and through which all data travels. Applications establish software networking sockets for a similar purpose — all data an application sends out and receives over a network connection passes through its socket.
Sockets provide a standard method for a program to establish network connections. Software developers can use an API to create a socket managed by the operating system so that they don't need to write their own way from scratch. When the application needs to send data out over the network, it writes that data to the socket as if it were writing a file to a disk. The operating system detects this and automatically forwards the data packet out over the network and to its destination.
Each socket has a unique socket address that combines an IP address and a port number. This address identifies both the specific computer the socket is running on and the application that created it. Applications running on a server create sockets when they launch and maintain them in a listening state, while applications on clients can open and close sockets as needed. While a socket is open, the operating system monitors it for incoming and outgoing data packets and looks at each packet's socket address to know where to forward it.
For example, when you visit a website with your web browser, it creates a socket that connects to another one on a remote web server using its IP address and port number (80 for HTTP connections and 443 for HTTPS connections). The browser sends a request for a specific webpage to this socket, which the operating system detects and forwards to the web server. When the web server sends the requested page back to your computer, the operating system looks at the socket address and knows to send it back to the web browser.
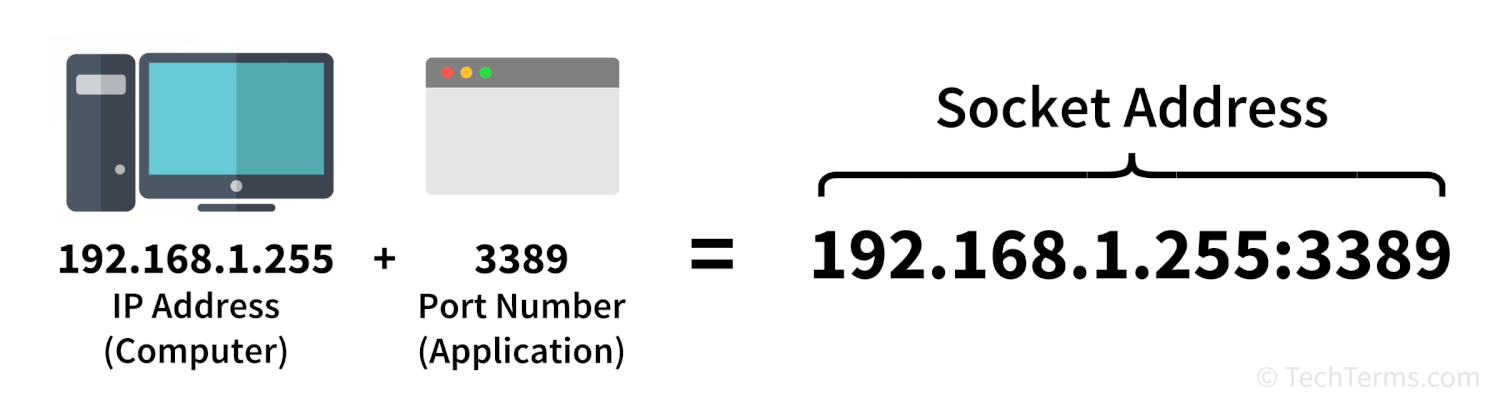
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge