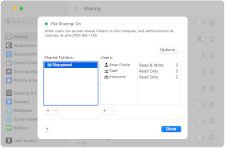
SMB
Stands for "Server Message Block."
SMB is a network communication protocol for file and printer sharing over a local or wide-area network. File servers use SMB to create shared folders that other computers can browse over the network just as easily as if they were on the computer's local disk. Only Windows-based computers use SMB sharing by default, but other operating systems can enable SMB support through software implementations like Samba.
The SMB protocol uses the client-server model to exchange data between computers. The client first requests access to a shared resource using the server's hostname or IP address. The server evaluates that request, then asks the client for authentication using a username and password. Once authenticated, the client can request specific files or other resources through additional messages to the server. The server uses SMB to break the files into packets for transfer, reassembling them on the client's disk.
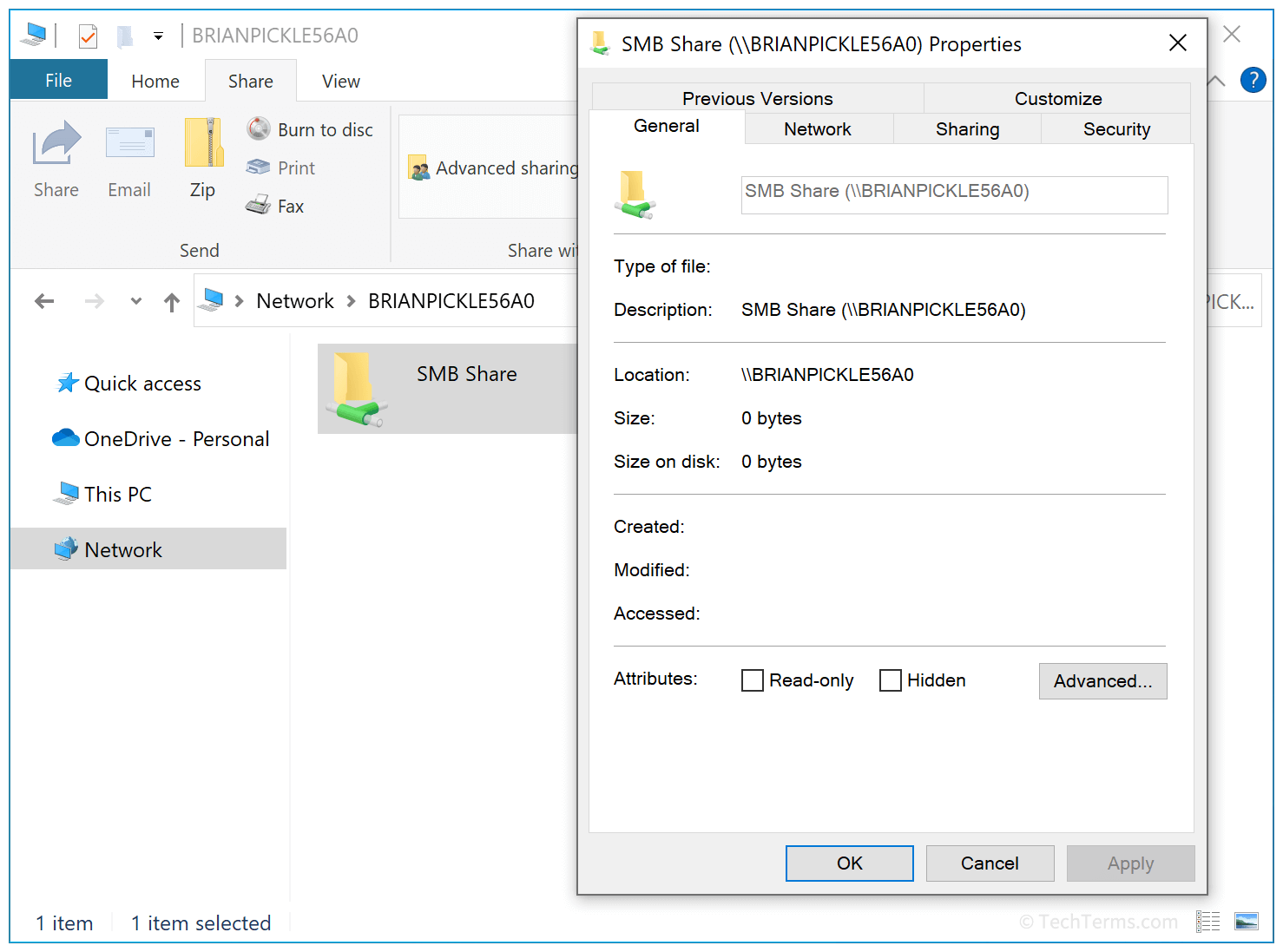
There have been several updates to the SMB protocol since its original implementation, offering increased security, reliability, and performance. The original version, SMB 1.0, was created to add network file sharing to DOS in 1983 and was later included in Windows. SMB 2.0 was released in 2006, adding stronger authentication while improving performance and reducing network overhead. SMB 3.0 came in 2012, adding end-to-end encryption for file transfers for increased security.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge