Raw Data
Raw data is unprocessed, unformatted data that has been collected and saved on a computer. Raw data serves as input for data processing tasks that turn it into useful information. Raw data may be generated automatically by a program, or someone may enter it into a computer manually.
Raw data files may consist of either plain text or binary data. For example, a router might keep a log of all network activity saved as raw data in a log file; a digital camera, on the other hand, saves raw image data into a binary Camera RAW file format. Regardless of the data type, raw data is often not very informative in its original state and depends on later processing and formatting.
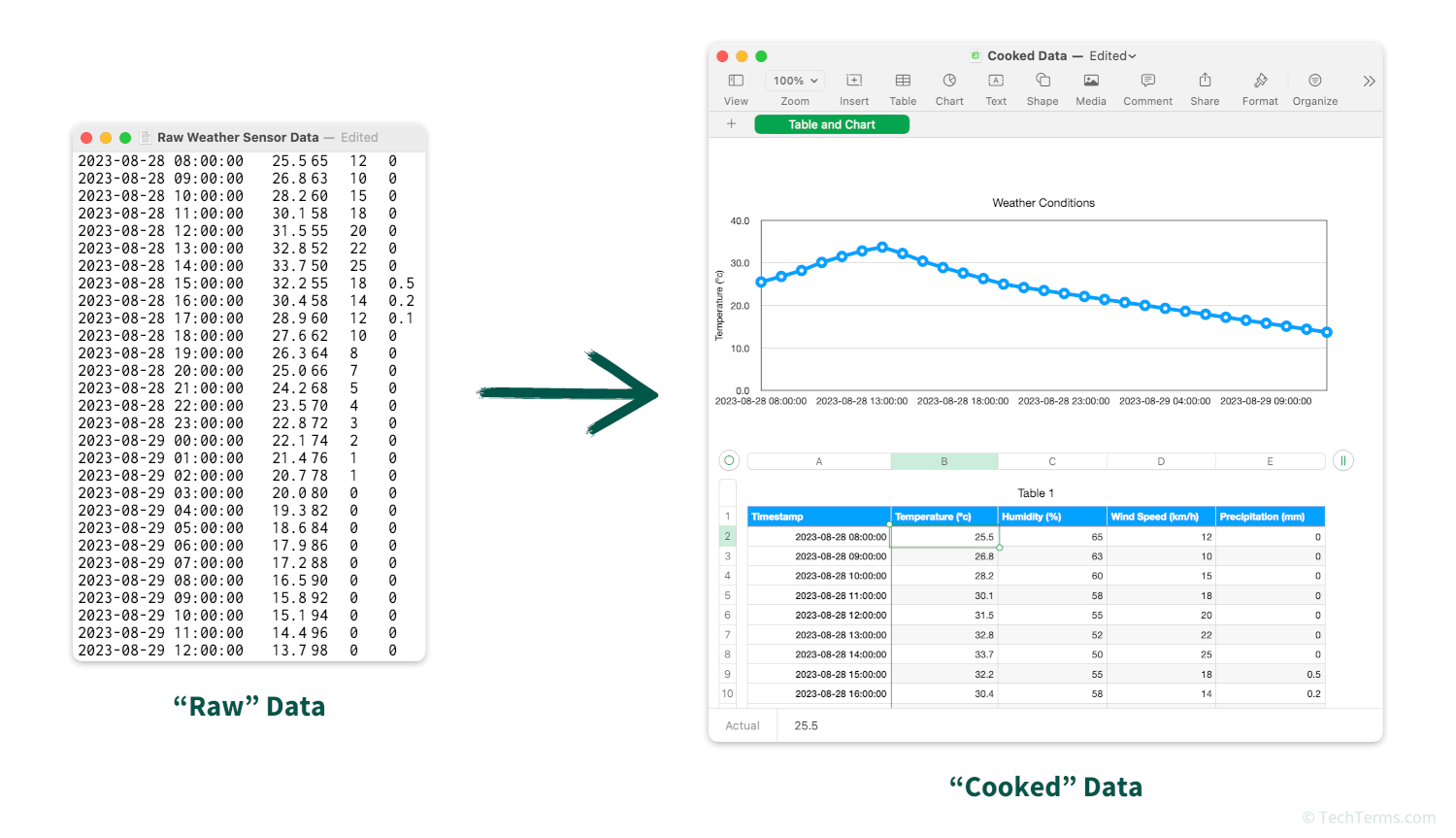
Files containing raw data may be human-readable at first glance — files produced by a computerized weather sensor may show numerical readings for temperature, humidity, and wind speed taken at regular intervals. However, this is still raw data because it has not been processed. In this case, processing could mean importing it into a spreadsheet application where you can fix errors, convert units, and create charts of the readings over time. Once you have processed raw data and converted it into a usable format, it is instead referred to as "cooked" data.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge