Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a document that stores data in a table of rows and columns. A spreadsheet assigns each column a letter (A-Z at first, then AA, AB, AC, etc.) and each row a number (1, 2, 3, etc.). It identifies each cell by its column and row (A1, B4, D8, etc.). A cell can store a unique value consisting of text and numbers, or even a formula that refers to the contents of other cells.
It is common to use the first row and/or column of a spreadsheet for labels describing the contents of the rest of the column or row. For example, a spreadsheet tracking customer information may keep each customer as a single row, with each column recording a piece of data about that customer, like their name, address, and phone number. When used this way, a spreadsheet is similar to a database.
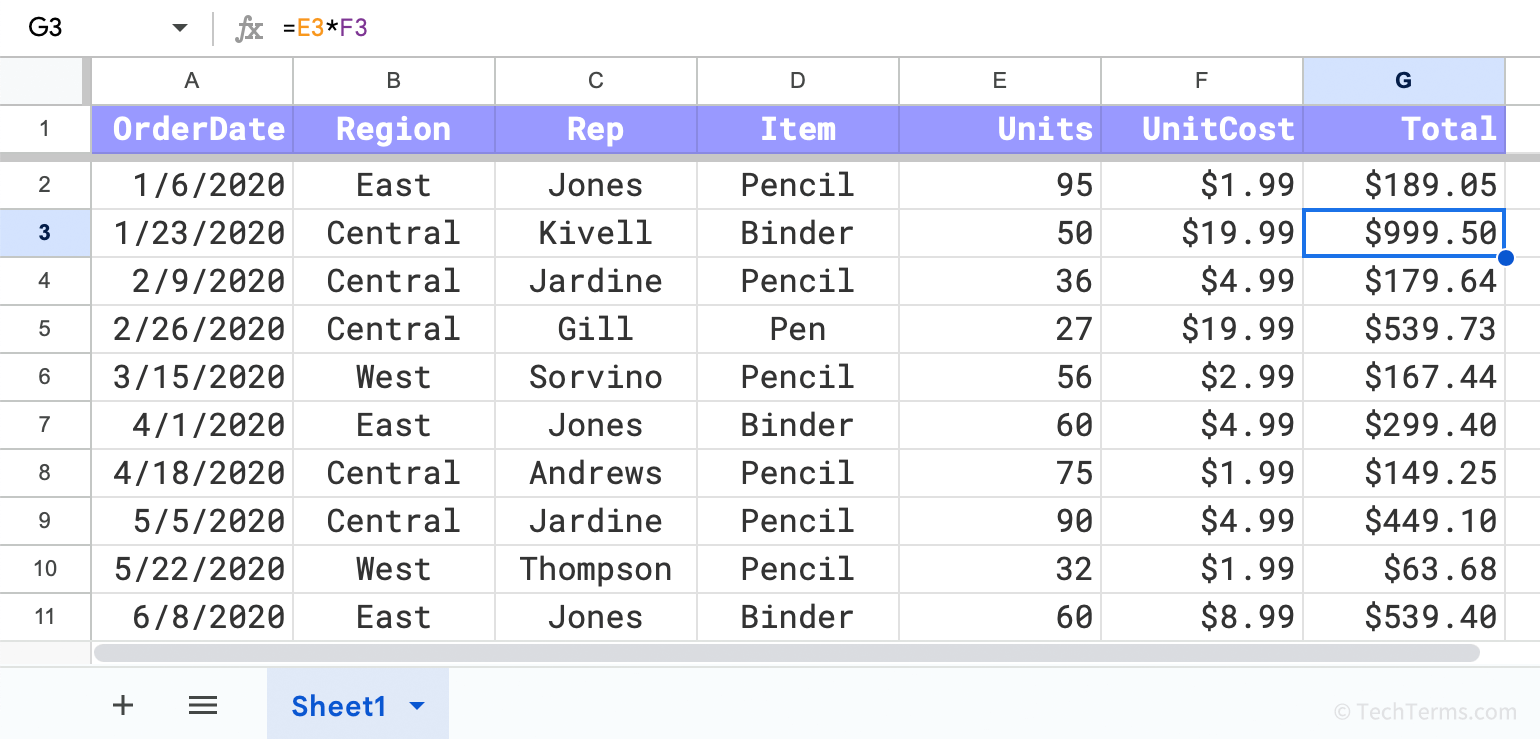
Spreadsheet cells may also contain formulas that reference the contents of other cells and perform calculations. Formulas may reference individual cells (C3) or cell ranges (B2:D48). Calculations also update automatically whenever a referenced value changes. For example, if a function calculates the average value of cells in a range, it will automatically update whenever any of those values change. Standard functions range from basic calculations like sums and averages to complex formulas like interest rate calculations. Because of their ability to quickly and easily process data, spreadsheets are often used for scientific and financial data analysis. They are also helpful for visualizing data by creating charts.
A spreadsheet file can contain multiple worksheets, which are separate tables containing separate batches of data. Formulas from one worksheet can reference cells on another worksheet, which helps keep data organized — for example, a spreadsheet that tracks sales data can keep each region on a separate worksheet while still calculating their quarterly results together.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge