MVC
Stands for "Model-View-Controller." MVC is an application design model comprised of three interconnected parts. They include the model (data), the view (user interface), and the controller (processes that handle input).
The MVC model or "pattern" is commonly used for developing modern user interfaces. It is provides the fundamental pieces for designing a programs for desktop or mobile, as well as web applications. It works well with object-oriented programming, since the different models, views, and controllers can be treated as objects and reused within an application.
Below is a description of each aspect of MVC:
1. Model
A model is data used by a program. This may be a database, file, or a simple object, such as an icon or a character in a video game.
2. View
A view is the means of displaying objects within an application. Examples include displaying a window or buttons or text within a window. It includes anything that the user can see.
3. Controller
A controller updates both models and views. It accepts input and performs the corresponding update. For example, a controller can update a model by changing the attributes of a character in a video game. It may modify the view by displaying the updated character in the game.
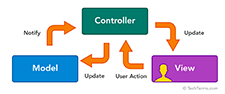
The three parts of MVC are interconnected (see diagram). The view displays the model for the user. The controller accepts user input and updates the model and view accordingly. While MVC is not required in application design, many programming languages and IDEs support the MVC architecture, making it a common choice for developers.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge