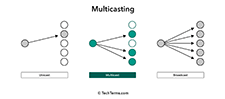
Multicast
A multicast is a transmission of data from a single source to multiple recipients. Multicasting is similar to broadcasting, but only transmits information to specific users. It is used to efficiently transmit streaming media and other types of data to multiple users at one time.
The simple way to send data to multiple users simultaneously is to transmit individual copies of the data to each user. However, this is highly inefficient, since multiple copies of the same data are sent from the source through one or more networks. Multicasting enables a single transmission to be split up among multiple users, significantly reducing the required bandwidth.
Multicasts that take place over the Internet are known as IP multicasts, since they use the Internet protocol (IP) to transmit data. IP multicasts create "multicast trees," which allow a single transmission to branch out to individual users. These branches are created at Internet routers wherever necessary. For example, if five users from five different countries requested access to the same stream, branches would be created close to the original source. If five users from the same city requested access to the same stream, the branches would be created close to users.
IP multicasting works by combining two other protocols with the Internet protocol. One is the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), which allows users or client systems use to request access to a stream. The other is Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM), which is used by network routers to create multicast trees. When a router receives a request to join a stream via IGMP, it uses PIM to route the data stream to the appropriate system.
Multicasting has several different applications. It is commonly used for streaming media over the Internet, such as live TV and Internet radio. It also supports video conferencing and webcasts. Multicasting can also be used to send other types of data over the Internet, such as news, stock quotes, and even digital copies of software. Whatever the application, multicasting helps reduce Internet bandwidth usage by providing an efficient way of sending data to multiple users.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge