Meta Search Engine
Meta search engines are search engines that search other search engines. Instead of maintaining their own index of web pages, a meta search engine sends user queries to multiple search services at the same time, then aggregates the results into a single list.
The first meta search engines, such as MetaCrawler, Mamma, and Dogpile, emerged in the 1990s. They searched indexes from Google, Yahoo, AltaVista, Ask Jeeves, and others, providing users with custom-aggregated search results. However, the searches were often slow, and the quality of the results was mixed. In the early 2000s, most Internet users switched to Google because of its speed and targeted search results.
Today, most meta search engines focus on specific industries and offer comparisons by pulling data from multiple sources. Common examples include:
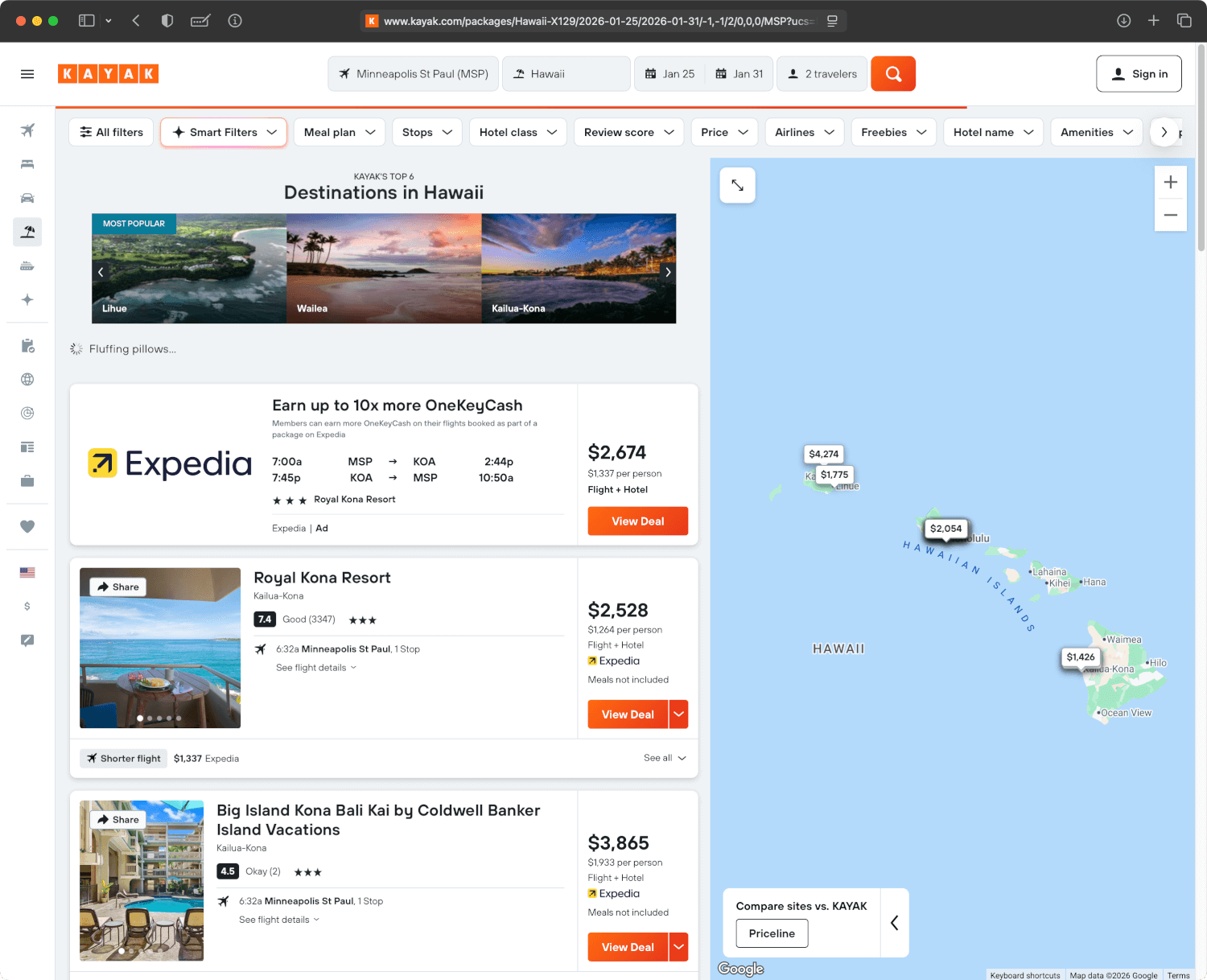
- Travel meta search engines that compare hotel prices, flights, or rental cars across multiple booking sites (e.g., Kayak, Trivago, Skyscanner)
- Shopping meta search engines that search several online retailers to compare prices and availability (e.g., Google Shopping, Shopzilla, PriceGrabber)
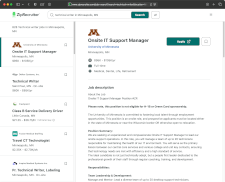
- Job search meta engines that aggregate listings from company sites and job boards (e.g., ZipRecruiter, Indeed, SimplyHired)
- Academic or research meta search tools that query multiple scholarly databases at once (e.g., Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar, BASE)
NOTE: While "meta searches" can broaden the scope of the search, the results are not always better than those from a single, well-tuned search engine. It's best to run similar searches across multiple search engines and choose the one that returns the best results.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge