Search Engine
A search engine is a web-based software tool that helps locate information on the Internet. A search engine first creates an index of web pages using page titles, content and other metadata. When a user enters a query into a search engine, it looks for matching pages in its index, runs an algorithm to rank what it finds, then presents a list of results. This results page is also known as a Search Engine Results Page, or SERP.
Search engines build their indexes using small software tools called "web crawlers" or "spiders." Spiders visit web pages, scan their contents, then follow hyperlinks to other pages. They crawl and index not only the titles and keywords of web pages but also the contents of images, videos, and other documents. They will also analyze backlinks, or links from one website to another, to determine which pages are considered more authoritative than others. Some search engines use the search history of the person running the query to weigh results differently based on what that person has clicked on in previous searches.
Different search engines not only use unique methods to index pages and rank results, but they can also have distinct purposes. Google, Bing, and Yahoo are general search engines that account for the majority of worldwide searches. Some countries have their own dominant search engines, such as Baidu in China and Yandex in Russia. Other search engines, like DuckDuckGo and Brave, place a higher priority on privacy and anonymity and will not keep records of their users' search histories.
Using Search Operators
Search engines support a set of boolean operator words that are used to refine a search. They help narrow a search down by telling the search engine what to prioritize and what to exclude. Some common operators are listed below.
- Quotation marks " " around a phrase will search for those words exactly as entered. The words must be next to each other, in that order and without other words in between.
- The word AND (or an ampersand &) between words will search for them together. Most search engines treat this as default behavior, but it can be used with other operators.
- The word OR (or a vertical bar |) between two words will search for pages containing either or both.
- A hyphen - before a word will exclude it from the search.
- An asterisk * is used as a wildcard that can represent any word or multiple words.
- Parentheses ( ) contain a set of operators and keywords that are treated as a single object when used with other operators.
- The phrase site: followed by a domain will limit results to pages in that domain. For example, searching site:techterms.com search engine operators will lead you to this page.
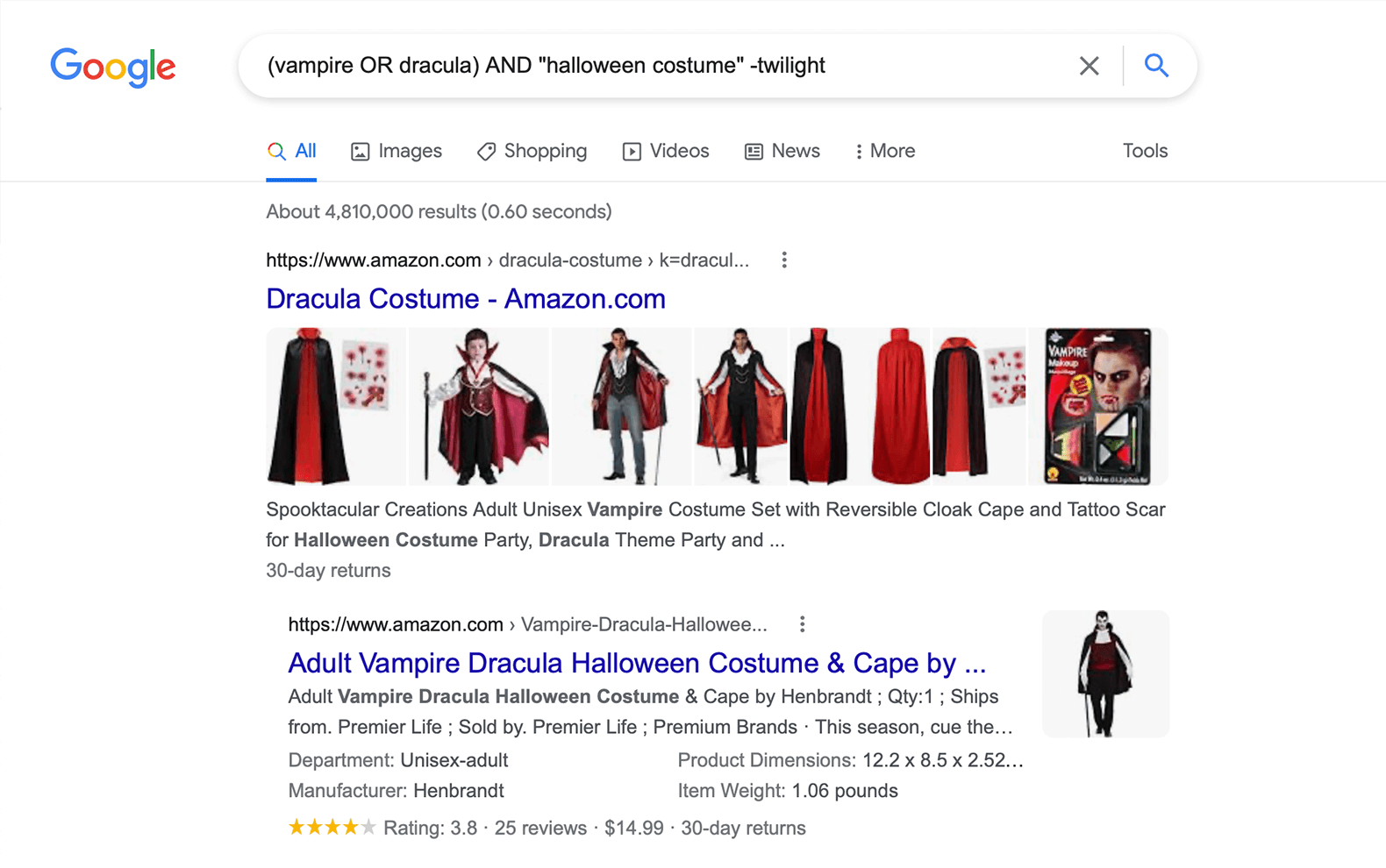
Combining several operators together can help focus a search. For example, entering (vampire OR dracula) AND "halloween costume" -twilight should show some spooky results.
NOTE: Operators like AND and OR must be entered capitalized in order to modify a search.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge