Media Compression
Media compression reduces the file size of audio, video, and image files through the use of media-specific compression algorithms. Unlike standard file compression algorithms like ZIP or RAR, which reduce file size while perfectly preserving the file data, media compression algorithms are designed specifically for the type of data they compress.
Most popular image file formats use some form of media compression. JPEG compression is a lossy method designed for photos that reduces subtle color variations to lessen the complexity of the image. GIF compression uses indexed color to reduce an image's color palette to 256 colors or fewer. PNG image compression uses a lossless algorithm that filters the image data and predicts the color of a pixel based on nearby pixels.
Audio compression codecs also attempt to remove imperceptible data to save file size. Lossy audio compression formats like MP3 and AAC remove unnecessary parts of an audio file — sounds too quiet or high-pitched for the human ear to hear. Lossless audio codecs like FLAC instead identify patterns in an audio signal that can be compressed and recreated perfectly. Lossy codecs result in significantly smaller file sizes, but lossless codecs preserve the entire audio signal while modestly reducing file size.
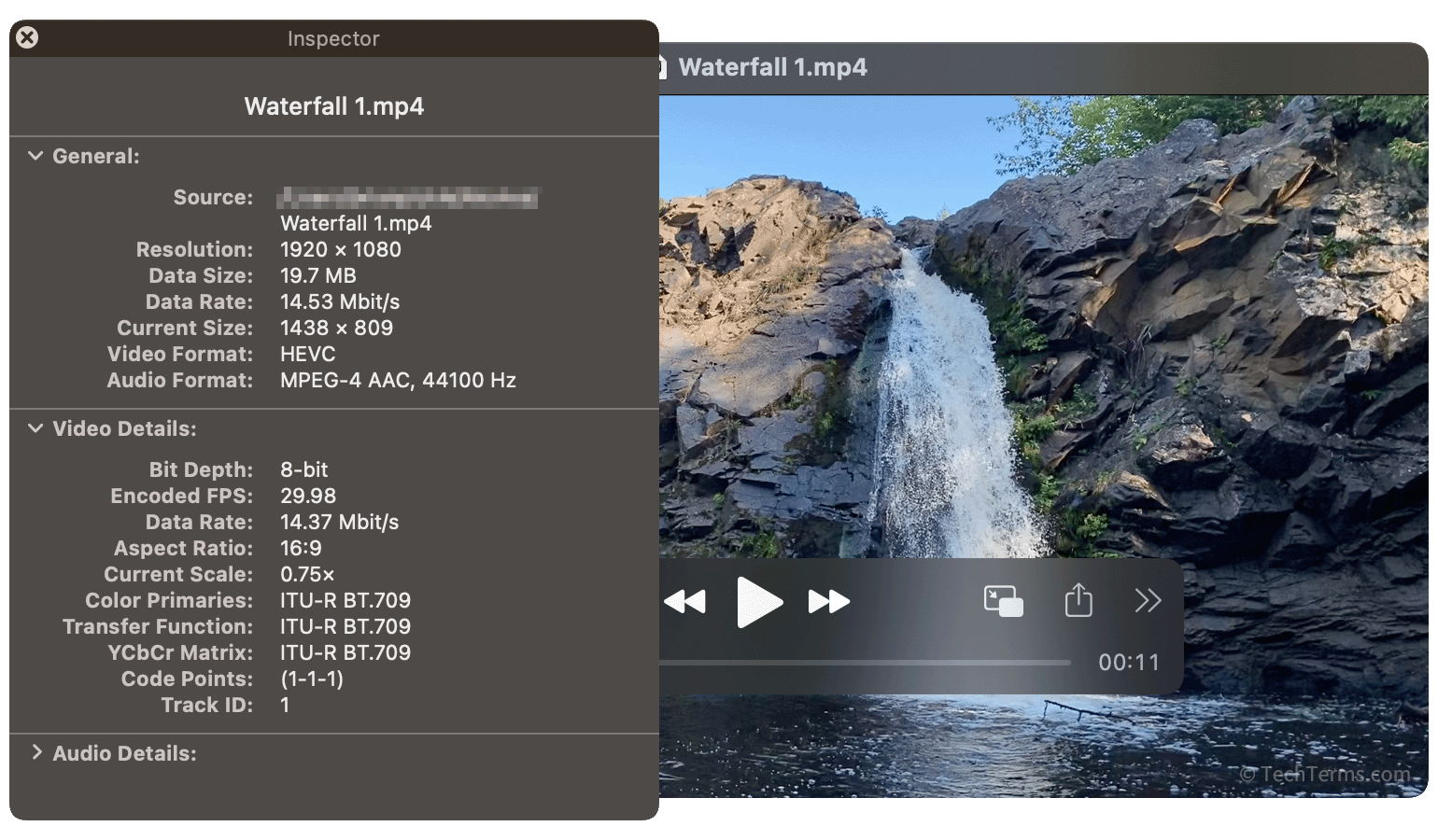
Since video files are much larger than images and audio files, most video codecs use lossy compression to save space. Video files may contain multiple data streams — the video itself, multiple audio tracks, and subtitle and caption tracks. Video codecs like H.264, H.265, AV1, and VP9 use a technique called inter-frame compression, which analyzes the differences between frames and only encodes the areas that change. Meanwhile, audio tracks use standard audio compression formats like AAC. Finally, compressed video and audio streams are combined into a container format like MKV, MP4, or AVI for distribution.
NOTE: In order to play back compressed media, a computer must have the necessary codecs installed.
Related file extensions: .JPG, .GIF, .PNG, .MP3, .M4A, .AAC, .MP4, .MKV, .AVI.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge