H.264
H.264, also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), is a codec for compressing high-definition video. H.264-encoded video is used for multiple applications like streaming movies and television programs, video conferencing, and storing video on Blu-Ray discs. It requires roughly half the bitrate of an MPEG-2-compressed video at the same level of quality, offering HD (1920 x 1080) video at 4 to 8 Mbps.
Like most other video codecs, H.264 uses lossy compression to discard unnecessary information from a video stream, shrinking the file size and bitrate of the resulting video. It uses a method known as inter-frame compression that breaks each frame into macroblocks, or 16x16 pixel squares. For each macroblock, the encoder analyzes the differences between the current frame and the previous one (known as the reference frame) and identifies the regions that have changed. The encoder then encodes only the differences between the frames. This way, scenes with little movement or a static background will need very little data per frame.
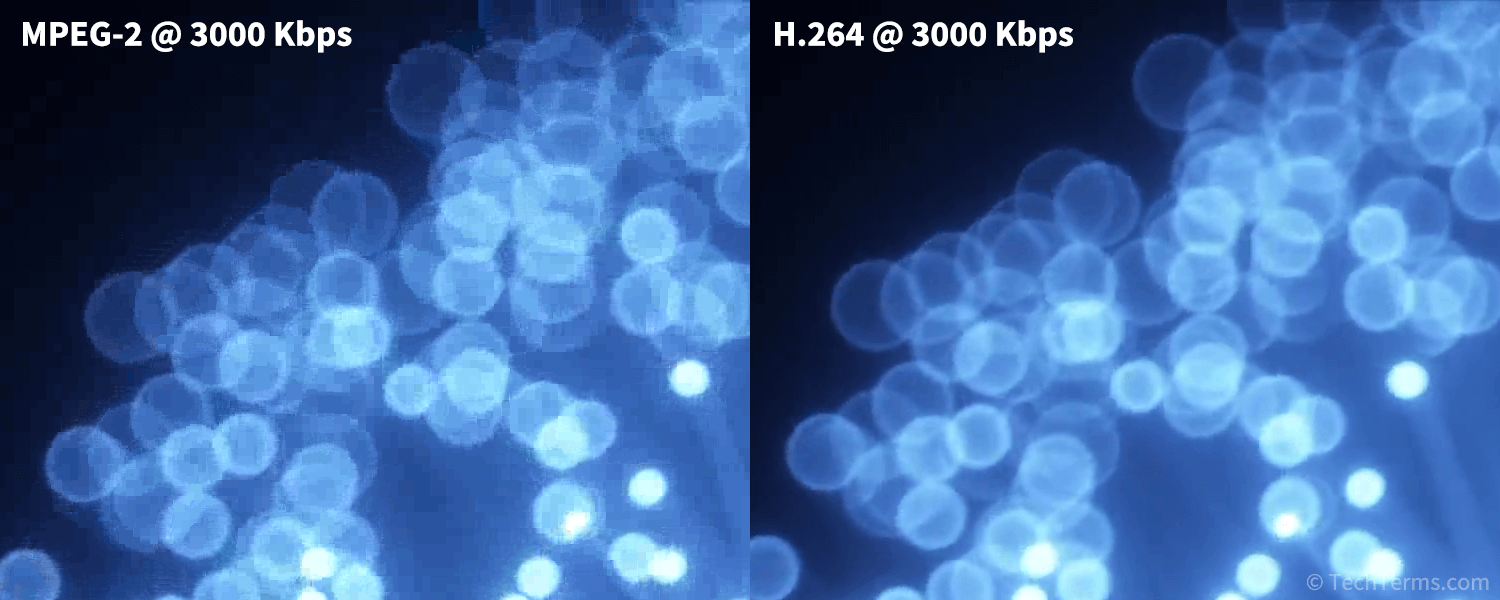
H.264 video compression uses considerably less data than previous compression standards. However, it requires much more computing power to decode a video stream. Most modern CPUs and GPUs include built-in support for H.264 decoding. Even though the format supports resolutions up to 8K, most H.264 decoding software is limited to HD video. Higher-resolution 4K video, as well as HDR video using 10-bit color, instead uses the more efficient successor format H.265 to achieve similar levels of quality at an even lower bitrate.
NOTE: H.264 is a codec, not a file format. H.264-encoded video is instead saved in a container format like .MKV or .MP4.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge