GUID
Stands for "Globally Unique Identifier."
A GUID is a 128-bit number that uniquely identifies something on a computer system. Each GUID is generated algorithmically and provides an identification string, similar to a serial number, that no other object on any system is likely to have. Programs often use GUIDs to create distinct IDs for database records, user accounts, transactions, security tokens, hardware devices, and many other objects.
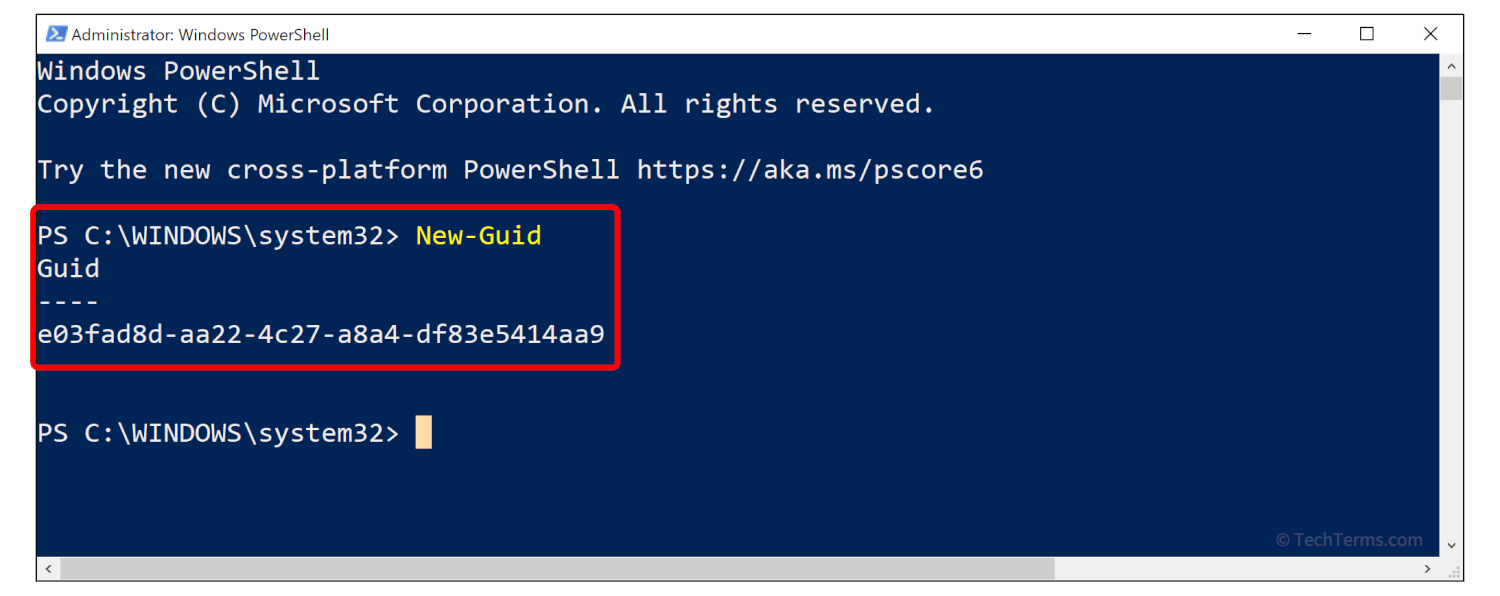
A GUID consists of 32 hexadecimal digits arranged in groups (8-4-4-4-12) separated by hyphens. Below is a typical example of a GUID:
9AC1A6F1-4A87-4624-B5F5-B74D494E21E0
While each GUID is meant to be completely unique, that uniqueness does not come from any central authority — there's no big database keeping track of GUIDs to guarantee there aren't duplicates. Instead, an individual GUID is likely to be unique due to the gigantic address space allowed by 128 bits of data (more than 340 trillion trillion trillion possible values). You could generate a billion GUIDs per second, and it would still take more than a trillion years to run out of address space.
The GUID specification outlines several standard versions that each use several factors to increase the likelihood that the result is unique. Version 1 and 2 GUID generators use a timestamp and the device's MAC address as seed values. Version 3 and 5 generators create a GUID by combining a namespace identifier and name given to the object, then hashing the result using either MD5 or SHA-1 algorithms. Version 4 generators use a random or pseudo-random number generator to create GUIDs without including time- or device-specific information. Most programming languages have GUID-generating code libraries that developers can use in their programs, and GUID-generating apps and websites are commonly available.
NOTE: GUIDs are also known as UUIDs, and the terms may be used interchangeably. Microsoft prefers to use the term GUID on their platforms, while most other companies use UUID.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge