Extranet
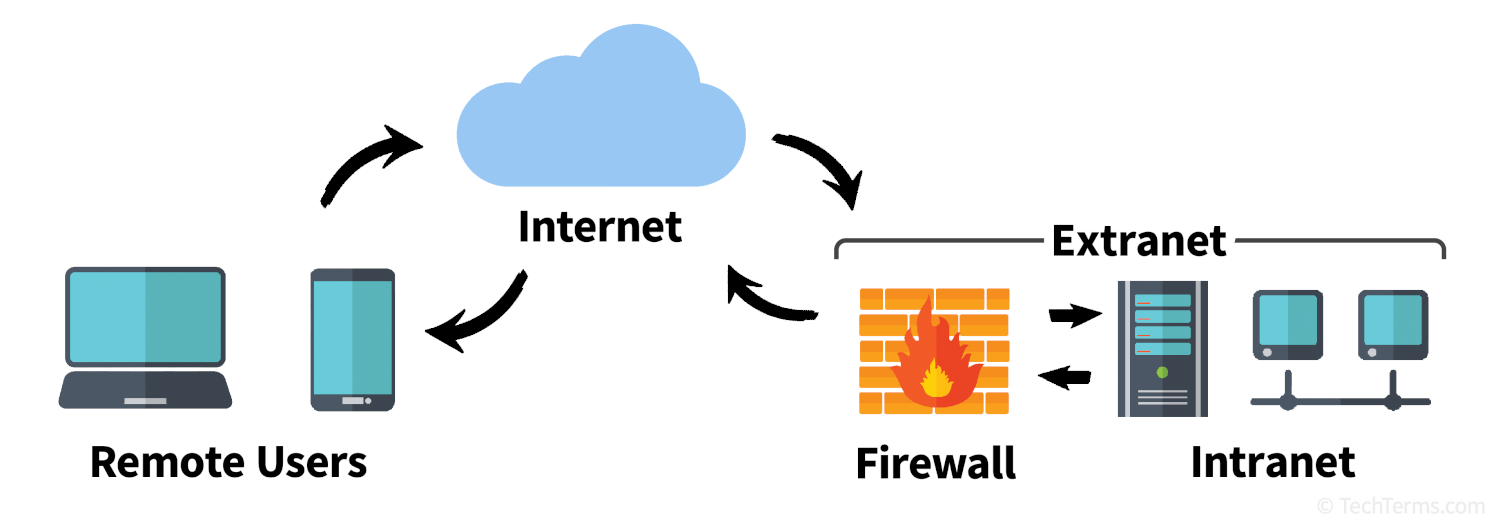
An extranet is a private intranet (or internal network) that is partially accessible over the Internet. It allows for limited and controlled access to resources on an intranet to users outside of a business or organization. Access to an extranet typically happens by visiting a web portal in a browser, and provides secure remote access to confidential information and intranet-specific applications.
Extranets use common networking technologies to provide outside users access to an intranet. An extranet may require simple authentication using usernames and passwords, or it may employ more secure multi-factor authentication methods that use mobile devices or password-generating hard tokens. Once the user is signed in, data transfers are typically encrypted using TLS; some extranets may even require the use of a VPN to provide extra security. Extranets often use firewalls to restrict incoming and outgoing network traffic, and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) watch for suspicious activity like repeated failed login attempts, blocking connections when necessary.
The use of extranets is not as widespread as it once was, thanks to the increasing popularity of SaaS and cloud computing platforms that move resources and applications off of intranets and into the cloud. However, extranets still have their uses and are common in certain industries. Customer portals are a common form of extranet, allowing customers to view their order history, track shipments, and interact with customer support. They're also common in supply chain management, helping suppliers and distributors communicate the status of orders and inventory. Finally, companies involved in joint ventures (like a construction company and an architecture firm working on a building) can use an extranet to share confidential information and track the status of their projects.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge