ARM
ARM is a family of 32- and 64-bit RISC processor architectures designed by Arm Ltd. and licensed to other companies to customize and produce. They are less expensive to manufacture than x86 processors, require less power, and produce less heat, making them ideal for compact devices. While they have historically been less powerful than x86 processors, some high-end ARM designs are now competitive against other desktop computer processors.
The ARM processor design is modular, which allows licensees to customize the processor designs to meet their needs. These customizations often include integrating other components like a GPU or cellular modem. This flexibility makes ARM a common system-on-a-chip (SoC) platform. After the licensee certifies the design with Arm (to ensure it still meets compatibility standards), they can manufacture their design themselves or with a manufacturing partner.
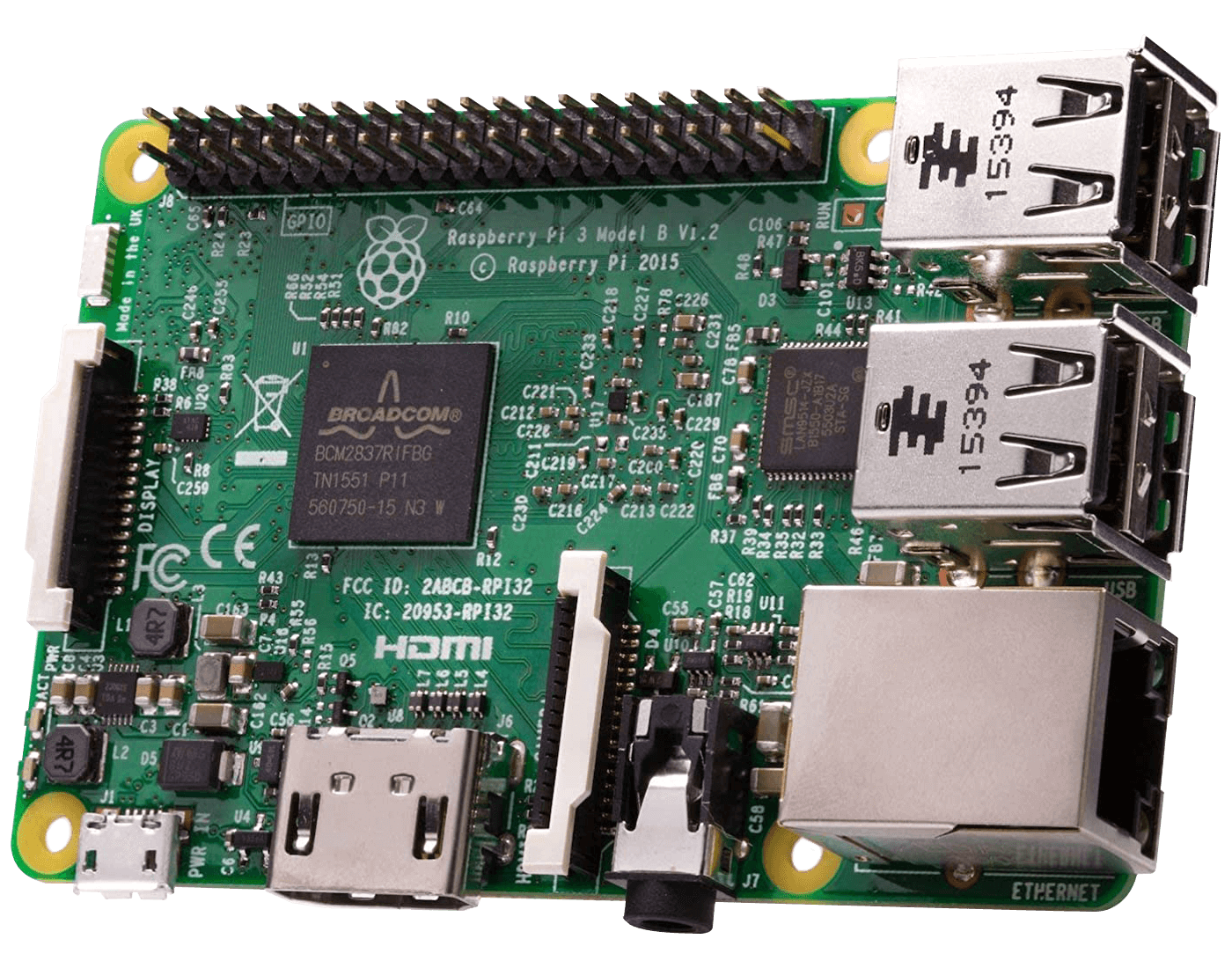
Many companies license ARM architecture for countless specialized purposes, from small embedded devices and smartphones to powerful desktop processors. For example, the Raspberry Pi uses a basic ARM processor design in a low-power computer on a single circuit board the size of a playing card. Meanwhile, Apple licenses only the ARM instruction set to produce their own designs for their A-series smartphone SoCs and M-series desktop processors.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge