Sound Card
A sound card is a hardware component in a computer that provides an interface for audio input and output. A typical sound card includes at least two 3.5mm audio jacks — one for analog stereo output and one for line-in or microphone input. It uses a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to convert digital audio into analog signals for playback through speakers and headphones; it also includes an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to digitize analog input from microphones. It may also include an interface for digital audio output, typically using a Toslink optical connector.
Many computer motherboards integrate a sound card directly, providing a set of 3.5mm audio jacks alongside the rest of the ports on the I/O panel. Dedicated cards that plug into a computer's PCIe expansion slot can add more input and output connections, improve audio processing performance, and improve audio quality when paired with high-end speakers. External sound cards that connect to a computer over USB, also known as audio interfaces, can include larger ports than would fit on an internal card's backplate, like ¼-inch audio inputs and XLR jacks for musical instruments and high-end microphones.
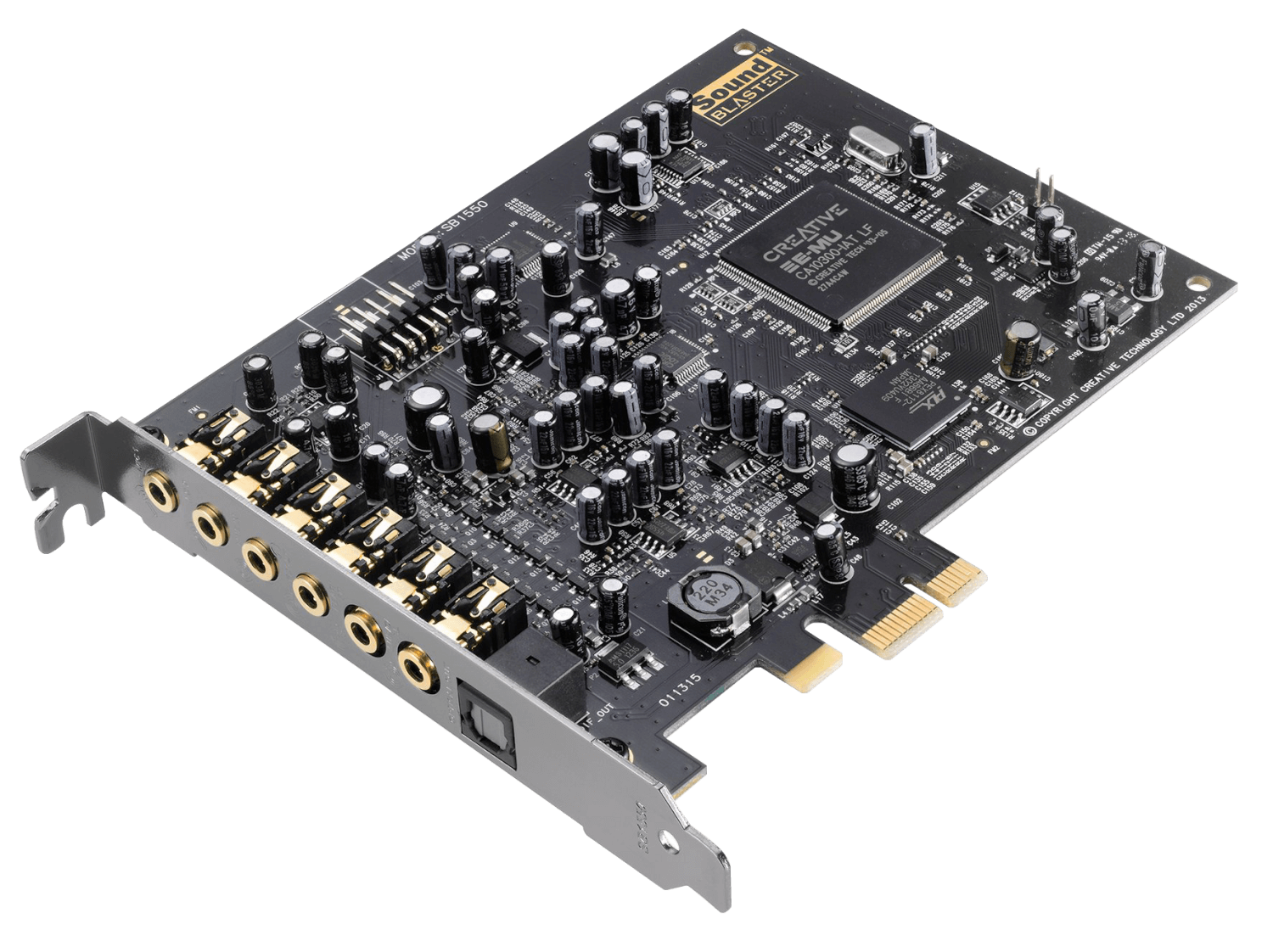
For most computer users, a motherboard's integrated sound card is enough to use with stereo speakers, headphones, or a headset with a microphone. However, there are several reasons that you may want a dedicated sound card. They often include a higher-quality DAC, which can produce cleaner sound with less noise. They may also provide better amplification to improve sound quality when used with high-impedance headphones. Dedicated sound cards often support higher resolutions and sampling rates (up to 32-bit / 384 KHz), and may even include hardware encoding and decoding for surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS.
NOTE: High-end sound cards often include breakout boxes. These devices connect to the sound card over a digital interface and provide more input and output jacks, a volume control knob, and a headphone amplifier.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge