Pharming
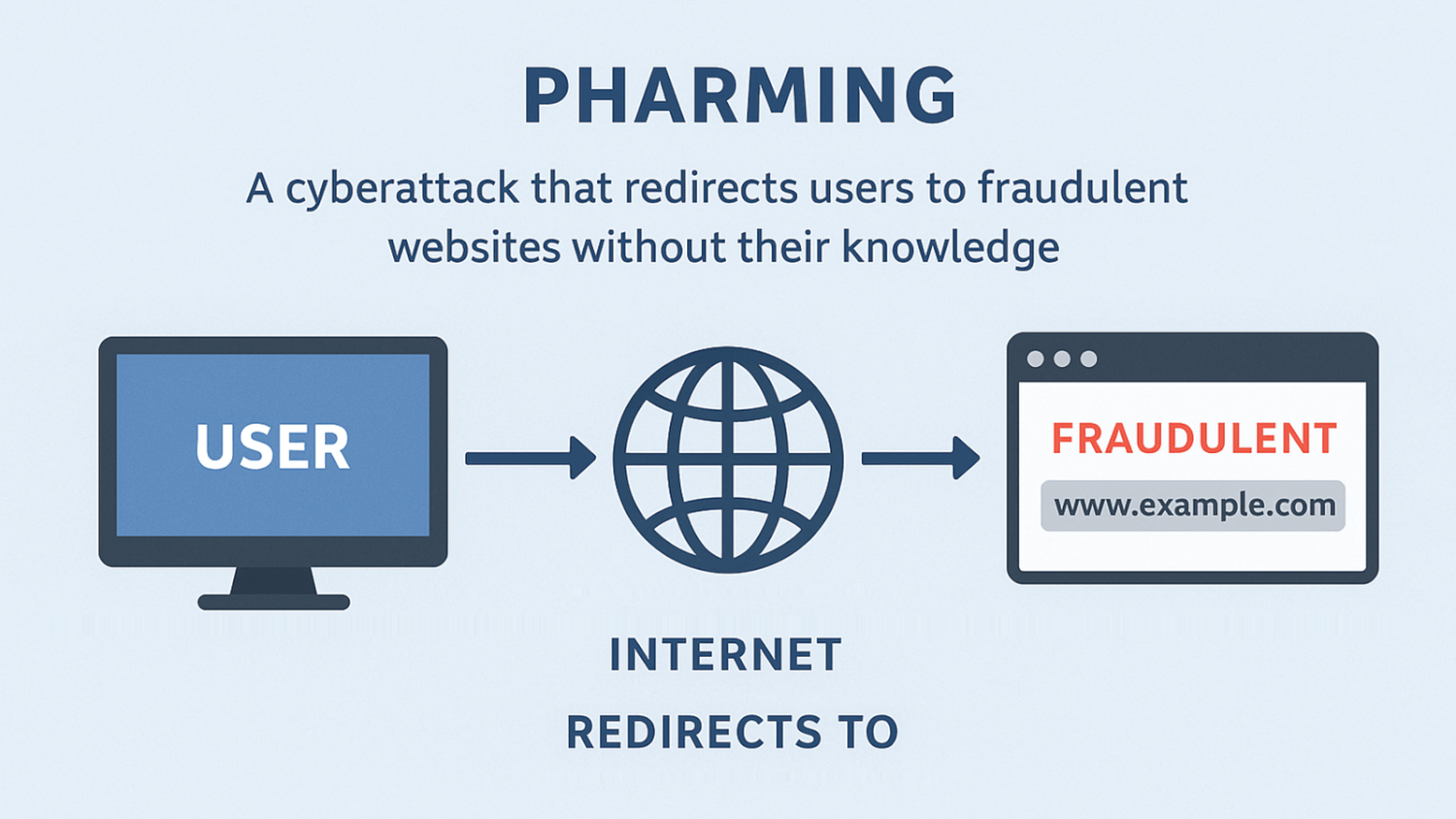
Pharming is a cyberattack that redirects users to fraudulent websites without their knowledge. Unlike phishing, which tricks people into clicking a fake link, pharming manipulates the underlying systems that route internet traffic, sending users to malicious sites even when they enter the correct URL.
Normally, when you type a domain name into your browser, the name is translated into a numerical IP address through the Domain Name System (DNS). Your browser then connects to the correct web server and loads the website. To speed things up, recent DNS lookups are often stored locally in a DNS cache on your device.
Pharming attacks interfere with this process in two main ways:
- Local pharming - Malware on a user's device modifies DNS settings or host files, redirecting legitimate domain names to malicious IP addresses.
- DNS server poisoning - Attackers compromise a DNS server, altering zone files so that all users relying on that server are redirected to fake sites.
Because DNS operates at the infrastructure level, pharming can be more dangerous than phishing, as it affects large numbers of users simultaneously. While modern DNS servers use security measures such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) to verify domain records, vulnerabilities still exist, and attackers continue to exploit them.
Protecting Against Pharming
You can reduce your risk by using security software to prevent local malware attacks and verify websites. If a familiar website looks suspicious:
- Clear your browser's cache or restart your device to refresh DNS entries.
- Run an antivirus or antimalware scan to check for local infections.
- Try visiting the site using a secure DNS provider (such as Google Public DNS or Cloudflare).
- If the problem persists, contact your Internet provider to report a potential DNS issue.
If you visit a site and something seems strange, don't enter any personal information. If it's a secure site (which nearly all sites are today), you can click the lock icon in the address bar to check the security details and make sure the certificate matches the site you intended to visit.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge