M.2
M.2 is a form factor for small internal expansion cards that plug directly into a slot on a computer's motherboard. It is most common in solid-state drives (SSDs) but is also often used to add Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or NFC expansion cards. The specification provides a computer bus interface for up to four PCI Express lanes, a single SATA port, or a USB connection. An M.2 card looks similar to a memory module, but with connector pins found on a short side instead of a long side.
While the M.2 format supports storage devices using a legacy SATA port, it is most commonly associated with NVMe SSDs. NVME drives utilize multiple PCI Express lanes for higher bandwidth and lower latency, offering read-write speeds up to 3.5 GBps (compared to 600 MBps over SATA).
Keys and Sizes
An M.2 slot on a motherboard is keyed with one or two notches, referred to by letters that indicate the location of the notch—the "A" notch removes pins 8-15, "B" removes 12-19, "E" removes 24-31, and "M" removes 59-66. The notches indicate what type of card that slot supports. Slots keyed A or E support wireless cards that add Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or NFC radios. Slots keyed B or M support SSDs at different speeds—slots keyed M support faster drives than slots keyed B.
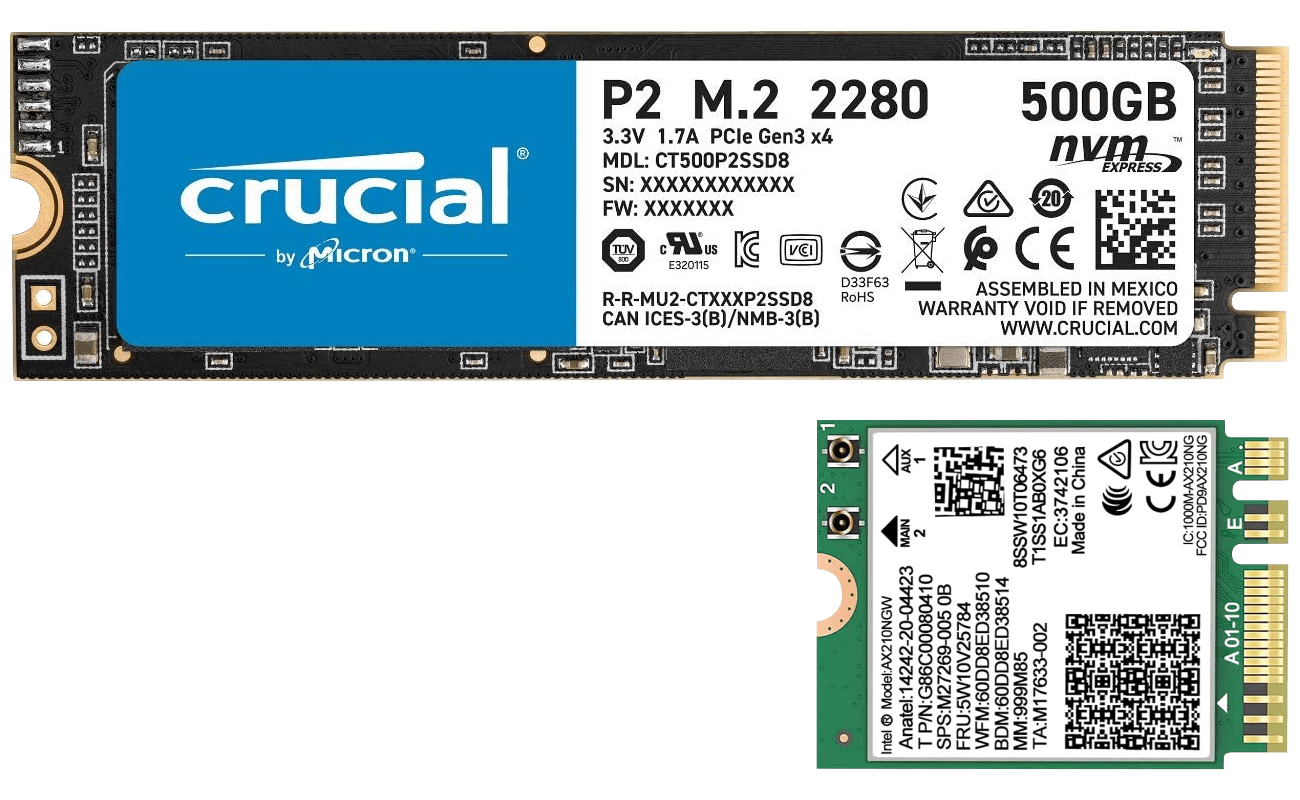
M.2 cards come in a standard size range, denoted by a 4- or 5-digit number. The first two digits indicate the width in millimeters, while the final two or three indicate the length. For example, a small Wi-Fi card may have a size of 2230 (22 mm wide and 30 mm long), while an SSD may have a size of 2280 or 22110. When installing an M.2 card, the end of the card must screw into a corresponding hole on the motherboard, so it is necessary to know what sizes the motherboard supports before installing a card.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge