LDAP
Stands for "Lightweight Directory Access Protocol."
LDAP is a protocol for accessing directory information services over a network. LDAP directory servers store information about user accounts, network-accessible resources, and other organizational data in a directory database optimized for fast information retrieval. LDAP is often used for authentication and permissions management in an organization, using tools like Microsoft Active Directory or IBM Directory Services. It functions over TCP/IP, which allows it to provide directory information over local networks and the Internet.
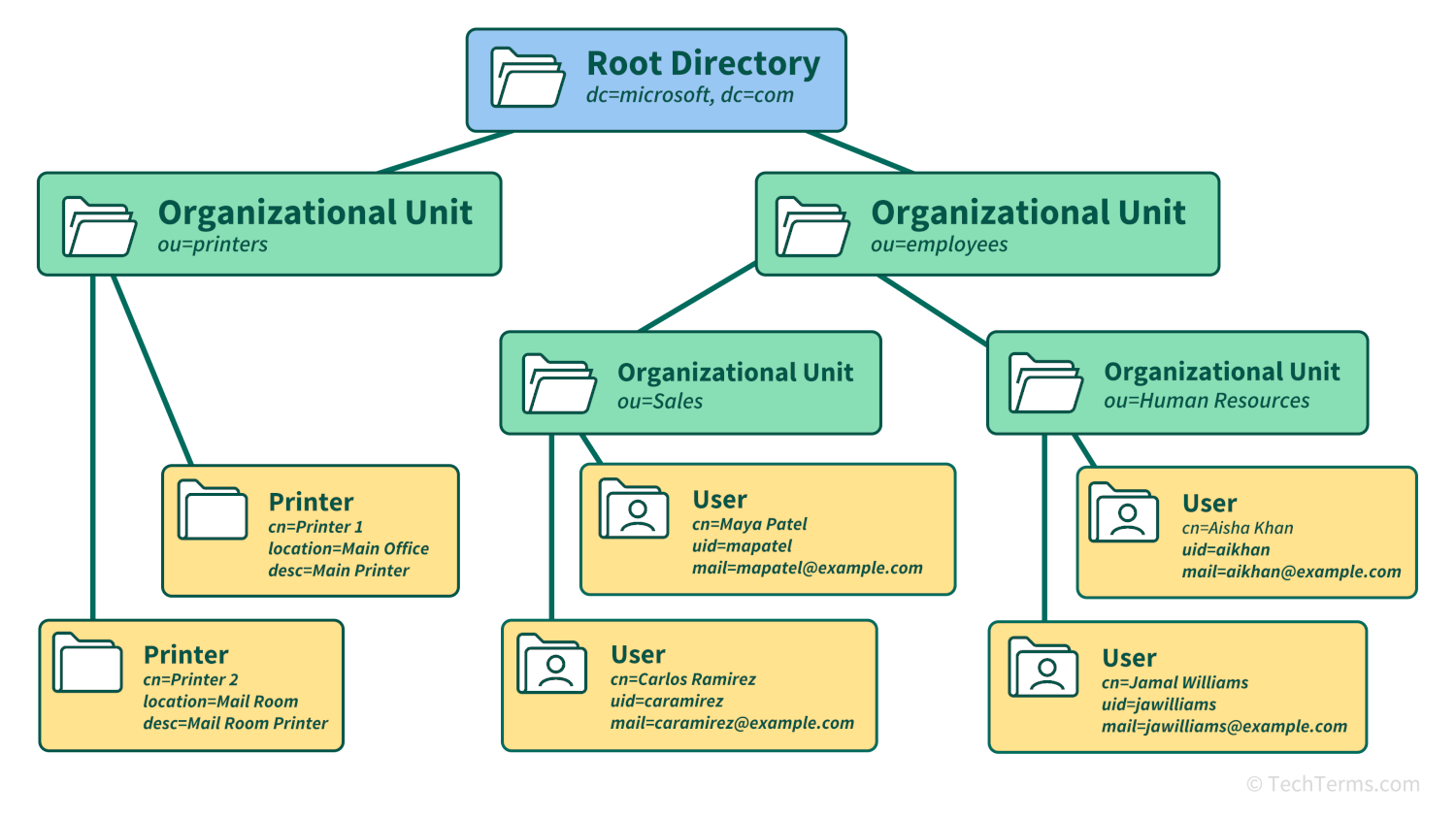
An LDAP directory server is like an organization's phone book, containing information that helps identify users and locate resources within the directory's hierarchy. Each directory is organized into several levels of a tree, starting at the root directory and split into branches — geographic locations, organizations, and organizational units like divisions and departments. Individual users within those divisions are further organized into groups and then assigned various attributes like user ID, email address, and permissions levels.
The most common reason for an application to communicate with a directory server using LDAP is for user authentication. For example, when a user wants to sign into a web app, that app makes an LDAP query that checks the provided username and password against what is in the directory and grants access if they match. Communication applications (like email clients, voice and video conferencing apps, and other collaboration tools) also use LDAP to provide an address book that allows one user to look up any other user in the directory system.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge