DMA
Stands for "Direct Memory Access."
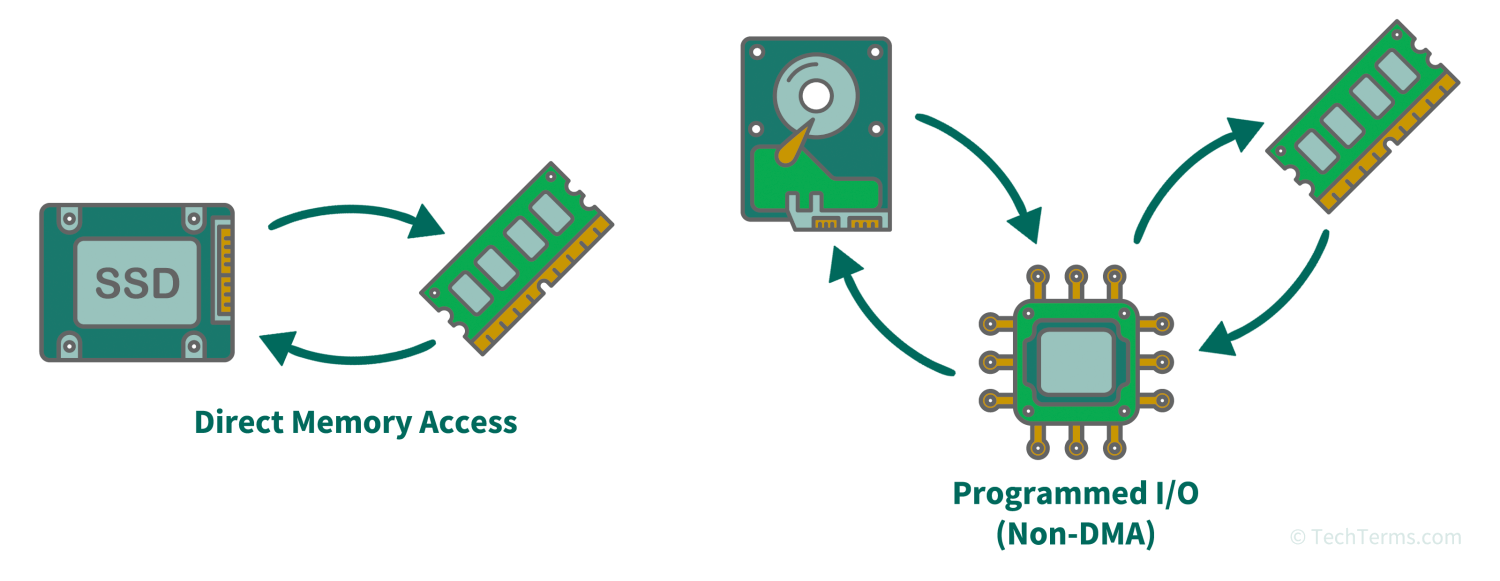
DMA is a method of transferring data between a computer's system memory and another hardware component that does not require the CPU to process the data. It uses the CPU only to initiate a data transfer; after that, the other component can communicate with the system RAM directly without any further involvement from the CPU. DMA reduces the overhead involved in data transfers, freeing up the CPU to continue processing other operations instead.
DMA is used by many types of hardware that have their own data processing capabilities. For example, a GPU rendering a 3D scene in a game uses DMA to load textures directly from system memory, leaving the CPU free to calculate physics and AI instead. Without DMA, the CPU needs to be involved in every read-and-write action, occupying processing resources that could be used for other tasks. Storage controllers, sound cards, and network interface cards also use DMA during data transfers.
Early computers used dedicated DMA controller chips to manage data transfers. These controllers assigned a limited number of DMA addresses to devices capable of DMA transfers. In modern computers, each DMA-compatible device includes an integrated DMA engine responsible for coordinating with other devices and managing data transfers over the PCI Express bus.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge