Digital Signature
A digital signature is a method of authenticating a message or document. A digital signature confirms that a message or document originated with a specific signer, and that it has not been altered since it was signed. They are often used with PDF documents, email messages, and word-processing documents to authenticate the signer and recipient.
Digital signatures require a form of identification, called a digital certificate, that authenticates the signer's identity. These certificates come from a certificate authority (CA), which validates someone's identity before issuing their certificate. Once you have a digital certificate, you can register it with applications that support digital signatures, like Adobe Acrobat (for signing PDF documents) or Microsoft Outlook (for signing email messages).
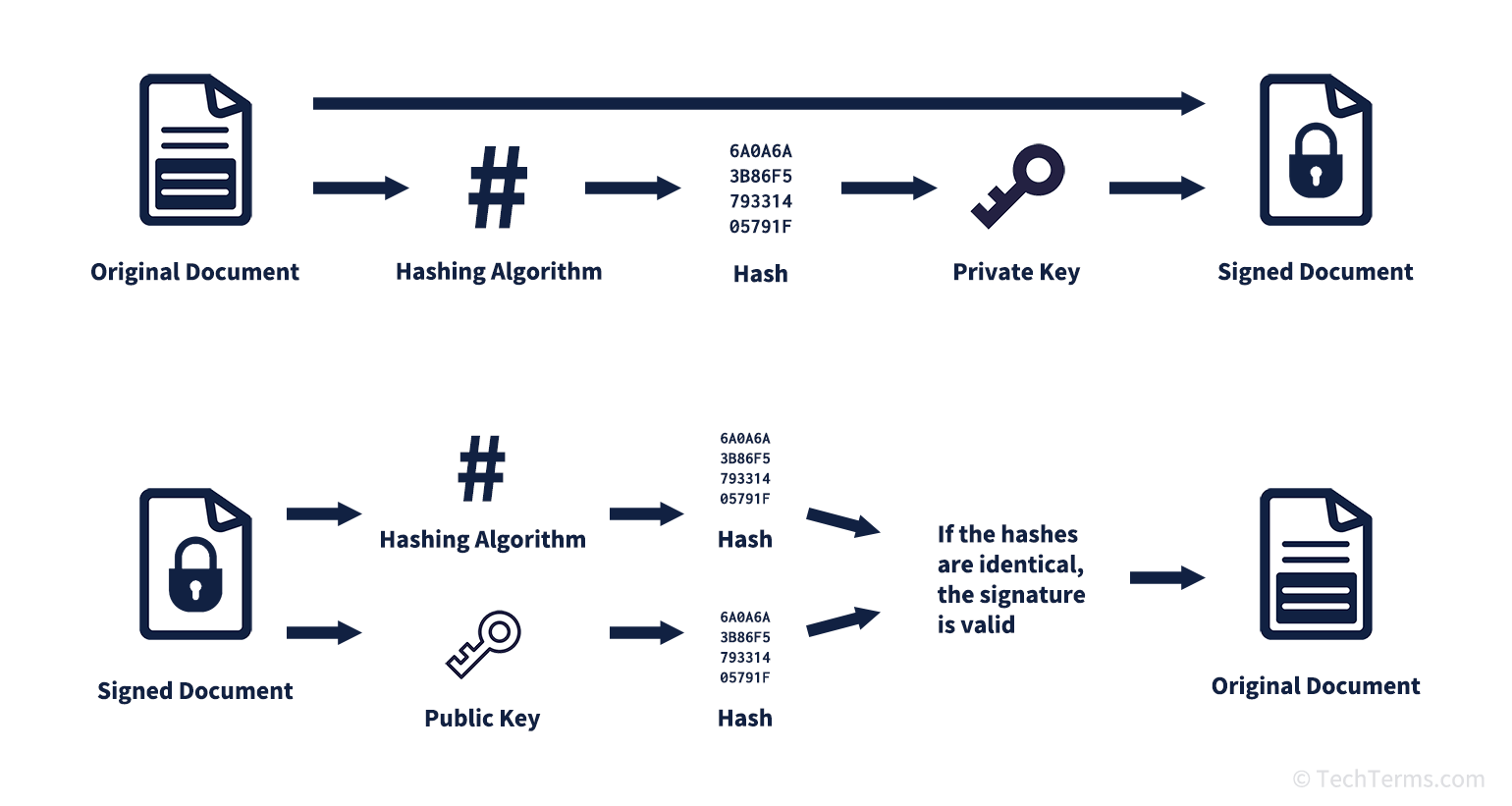
When you sign a message or document, the signing application first uses a hashing algorithm to generate a hash from the file, which is then encrypted using your private key. The application combines this value with your digital certificate and public key into the digital signature, then packages it with the document or message. Later, the recipient can verify your identity by decrypting the hash using your public key, then running the hashing algorithm on the received message or document. If the two hashes match, the message or document they received is identical to the one you signed.
In many countries, digital signatures are equivalent to handwritten signatures and carry the same legal weight. They may both certify and approve legal and business documents. The document's author creates the certifying signature to show that it has not changed since signing. Other signatories may add their approval signature later to indicate that they have read and approved the document.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge