Data Transfer Rate
A data transfer rate measures how fast data moves from one location to another. It can refer to the movement of data between disks, between other components like a CPU and RAM, or between two devices connected over a network. The maximum data transfer rate that a connection supports is known as its bandwidth, and the actual observed rate is called its throughput.
How a data transfer rate is measured often depends on the context. Telecommunication data transfer rates are measured in bits per second (bps). For example, a DSL internet connection may transfer data at 20 Megabits per second (Mbps), while a high-speed ethernet connection can go up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps).
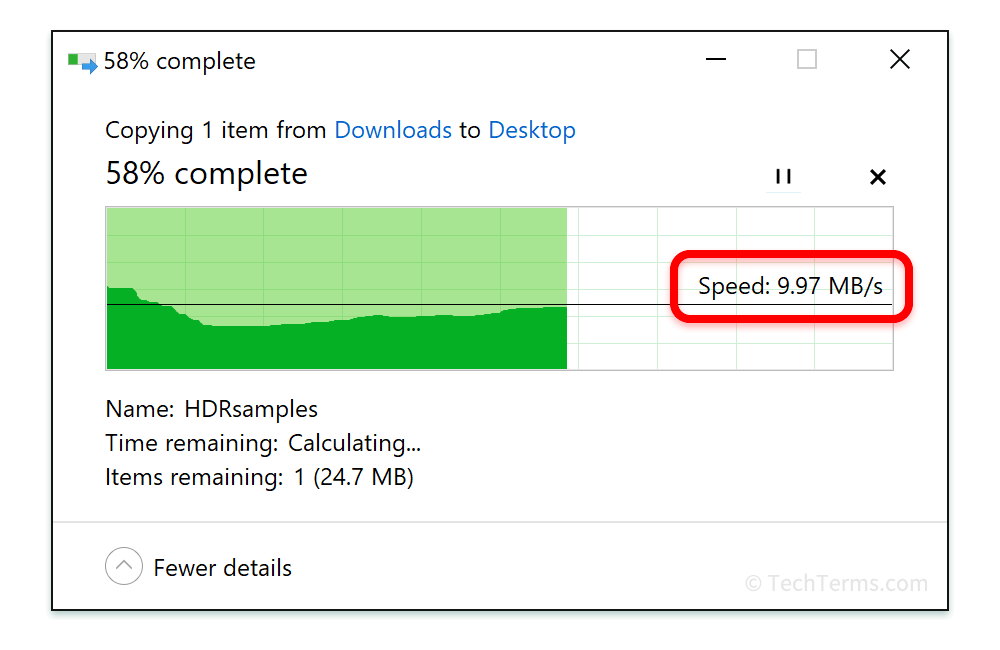
File transfer rates are instead often measured using bytes per second (Bps). For example, when you copy a file from a network drive to your computer, the Windows file transfer dialog box will show a number like 5 MB/s. Since a single byte is eight bits, you can convert between bits per second and bytes per second by multiplying by 8 (to go from bytes to bits) or dividing by 8 (for bits to bytes).
Data transfer rates often vary during a data transfer. Many factors, like congestion, interference, or distance, can affect a data transfer rate. For example, if you are not the only person copying files from another computer over the network, the data transfer rate you see will be lower than if you had the entire network to yourself.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge