Batch Process
A batch process is a computer process that performs a pre-determined series of commands on a group, or "batch," of data inputs. Batch processing data saves significant time by automating repetitive tasks consistently and repeatably. Once started, a batch process requires little or no input from the user.
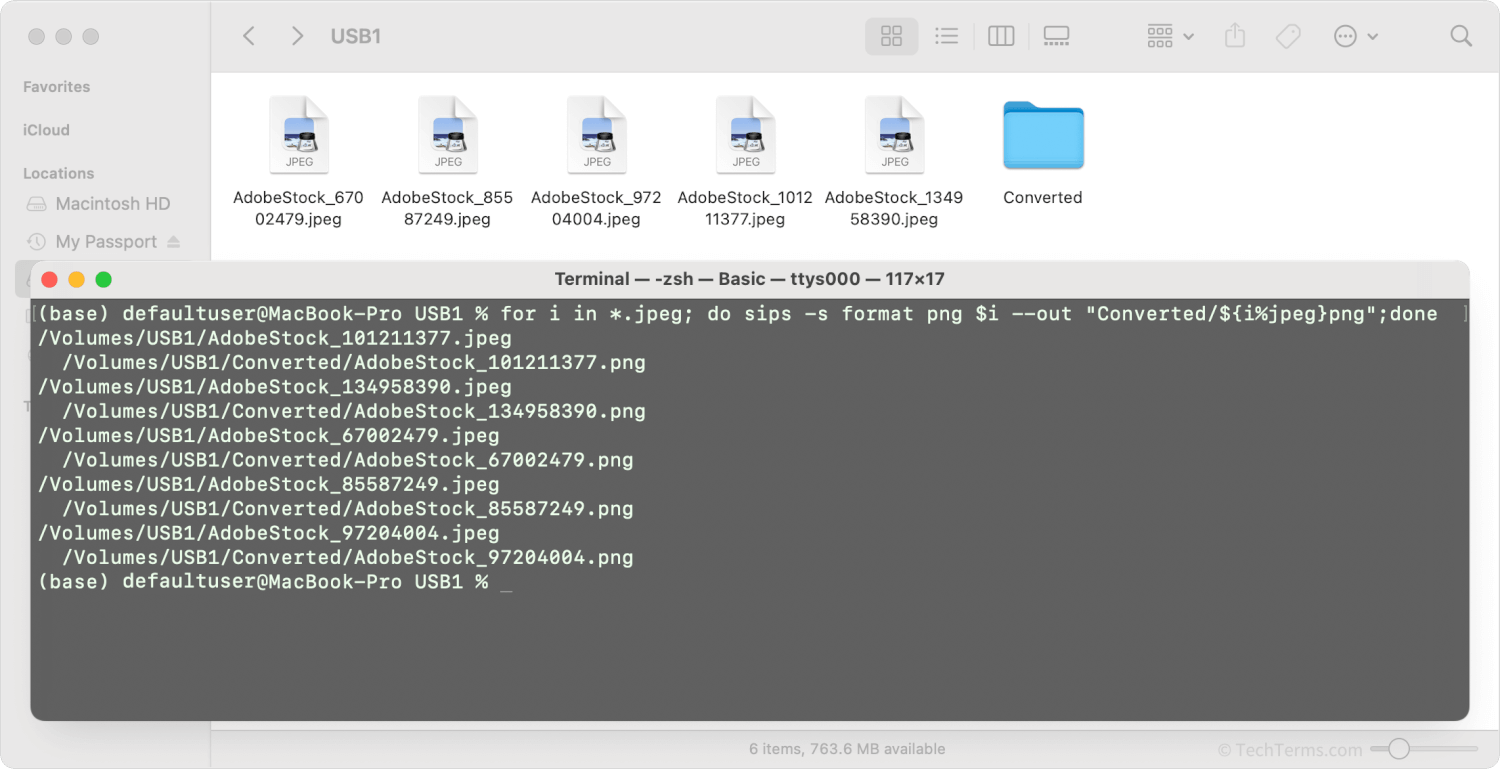
You can save commands to a script or batch file to run later, or enter them directly into an application or command line to run it immediately. These commands typically do not contain direct links to the data or files it processes; instead, you can use wildcard characters to set what kind of file or data you want to process within the batch. For example, a photographer can create a batch file that takes an entire folder of photographs as input, then creates copies in a new folder that have been resized to a specific resolution and renamed with the date and time they were taken. All they need to do is tell the application or operating system running the batch process which folder to use, and the rest happens automatically.
Batch processes, also known as jobs, may be scheduled to run one time or recur on a set schedule or interval. For example, a system administrator may write a batch file that backs up a specific local folder to cloud storage and then schedule that batch process to run every night. Unix and Linux include several task scheduling utilities — at schedules a job one time, while cron creates recurring tasks. Windows includes a Task Scheduler application that can run jobs at specific times or at regular intervals. In addition to cron and at, macOS supports job scheduling using the launchd utility; it also supports Quick Actions and Folder Actions that allow users to perform simple batch operations on selected files and folders.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge