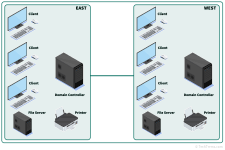
Domain
A domain is a group of computers on a network that can be centrally administered with a shared set of rules. Domains may be part of a local area network (LAN), a wide area network (WAN), or a virtual private network (VPN). Servers, known as domain controllers, manage users and user groups for every computer connected to their domains and are often used to manage large enterprise networks.
Domains can help map a company's organizational structure to its network by creating domains for individual departments, divisions, or regions. Users in a domain may log in to any workstation in their domain. Administrators can assign users to user groups and choose what resources those users and groups may access. For example, you can configure a domain so that one set of computers, printers, phones, and shared folders is available to all users, while another set of resources is limited to a single user group.
Domain controllers also enforce security policies and firewalls across a network and can restrict incoming or outgoing network traffic. Many domain controllers also act as DNS servers for their domains. They can assign hostnames to individual computers for identification instead of (or in addition to) IP addresses.
Domain controller software can run on several different platforms. Windows Server Active Directory is one of the most popular domain controllers, included as a component in the Windows Server operating system. Unix and Linux-based servers can use Samba Domain Controller, which is available as part of the Samba software suite.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge