Ping
A ping is a signal sent to a host that requests a response. It serves two primary purposes: 1) to check if the host is available and 2) to measure how long the response takes.
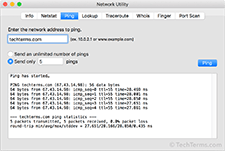
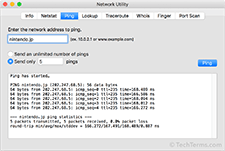
A ping request can be performed using a ping command, which is a standard command in most command line interfaces. Several network utilities provide a ping feature, which allows you to ping a server by simply entering the IP address or domain name. Most ping programs send multiple pings and provide an average of the pings at the end.
The ping itself consists of a single packet (often 32 or 56 bytes) that contains an "echo" request. The host, if available, responds with a single packet as a reply. The ping time, measured in milliseconds, is the round trip time for the packet to reach the host and for the response to return to the sender.
Ping response times are important because they add overhead to any requests made over the Internet. For example, when you visit a webpage the ping time is added to the time it takes a server to transmit the HTML and related resources to your computer. Pings are especially important in online gaming, where events happen in real-time.
While Internet connection speeds can affect pings, ping response time is often directly related to the physical distance between the source and destination systems. Therefore, a fast connection between New York and Tokyo will likely have a longer ping than a slow connection between New York and Philadelphia. Network congestion may slow down pings, which is why pings are often used for troubleshooting.
What is a Good Ping Response Time?
- < 30 ms - excellent ping; almost unnoticeable; ideal for online gaming
- 30 to 50 ms - average ping; still ok for online gaming
- 50 to 100 ms - somewhat slow ping time; not too noticeable for web browsing but may affect gaming
- 100 ms to 500 ms - slow ping; minimal effect on web browsing, but will create noticeable lag in online gaming
- > 500 ms - pings of a half second or more will add a noticeable delay to all requests; typically happens when the source and destination are in different parts of the world
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge