PHP
Stands for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor."
PHP is a scripting language web developers use to create dynamic websites. It is often installed by default on Apache web servers, alongside MySQL as part of a "LAMP" configuration.
Each PHP code snippet starts with <?php and ends with ?>. PHP pages may contain multiple snippets inserted throughout the HTML that generate dynamic content. When a website visitor accesses a PHP page, the web server processes, or "parses," the PHP code before sending the HTML to the client's browser. In the example below, the PHP function gets the local time and date from the server and inserts it into the HTML. ("F d, Y" formats the date as December 31, 2021.)
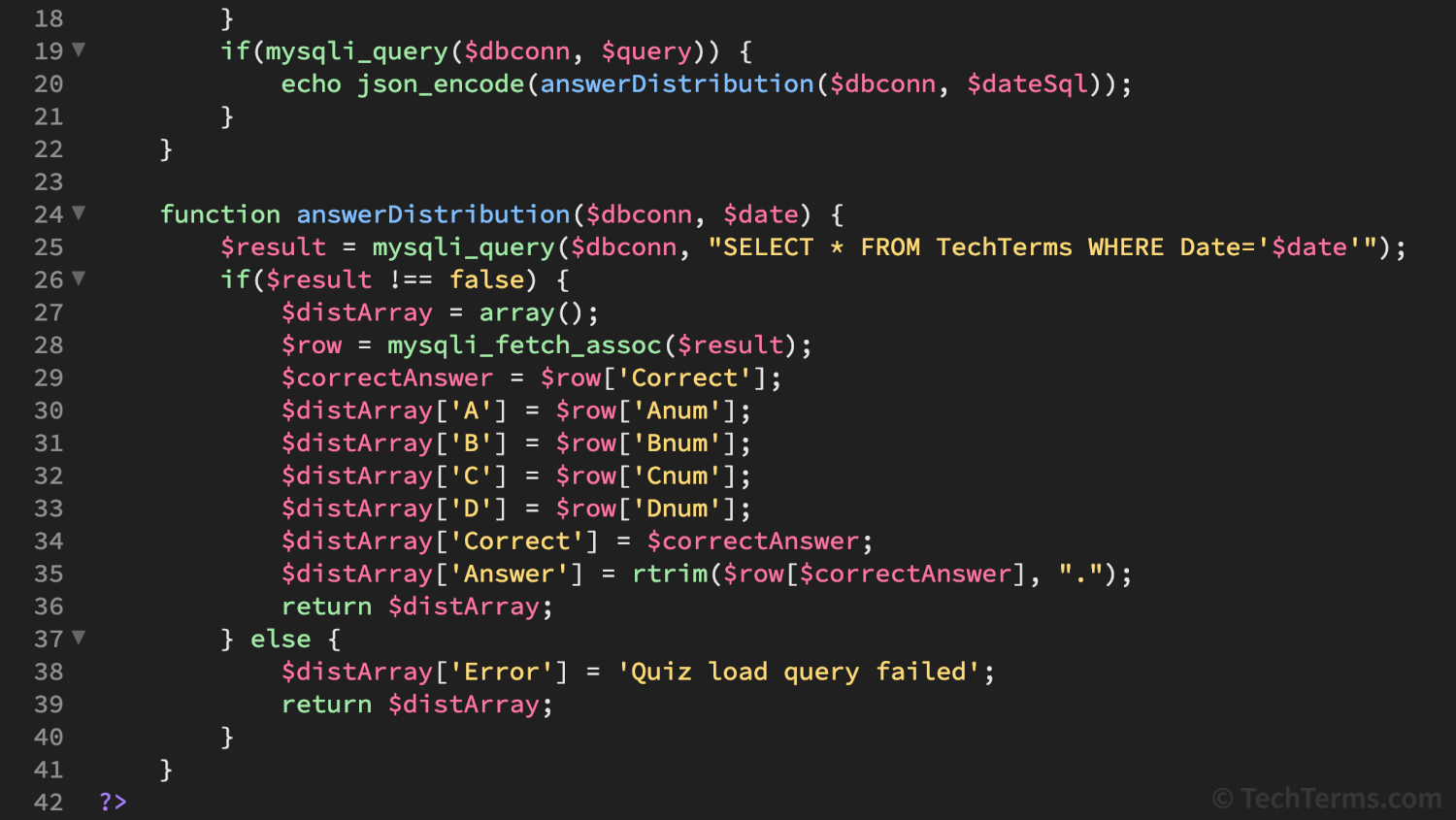
<p>The current date is <?php echo date("F d, Y"); ?></p>Below is a behind-the-scenes look at some of the PHP code used to generate quiz questions on TechTerms.com.
PHP scripts can range from simple one-line commands to complex functions. Some PHP-based websites generate nearly all webpage content dynamically using a series of PHP scripts. While early versions of PHP were not object-oriented, PHP3 introduced support for classes, including object attributes and methods. Developers can create custom object libraries and import them into various PHP pages, similar to a compiled language.
Much of PHP's syntax is similar to other languages such as C++, Java, and Perl. However, PHP contains several proprietary functions, including MySQL-specific methods for accessing records from a MySQL database. Because of its integration with MySQL, its consistent maintenance, and overall ease of use, PHP remains a popular choice for creating dynamic websites.
File extension: .PHP
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge