Archive
An archive file is a single file that contains multiple files and/or folders. Archives may use a compression algorithm that reduces the total file size. Some archive formats also include encryption to protect an archive's contents from unauthorized users.
Archives are useful for backing up multiple files and folders into a single file. They preserve the metadata for files they contain, like a file's created and modified dates. Consolidating a large number of files into one makes them easier to back up and share. For example, you can compress an entire vacation's worth of photos into a single archive, then send it to family members or a backup service. Since everything is in a single file, you don't have to worry about missing any photos. If the archive format supports compression, it will also reduce the total file size of the archive compared to the individual files.
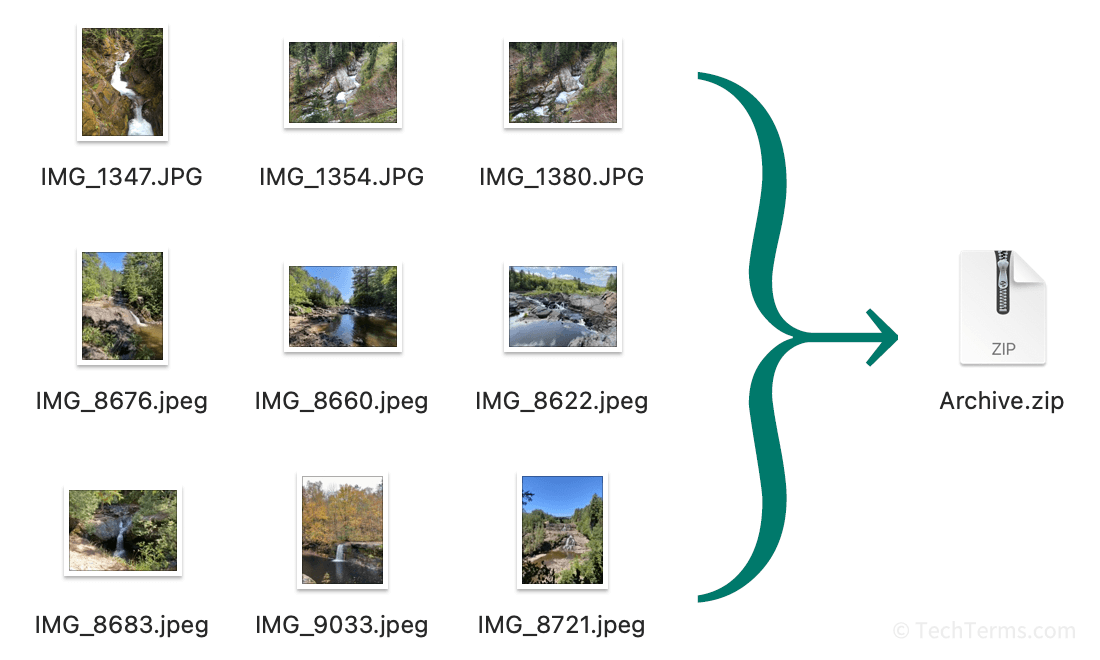
Most operating systems include built-in utilities that can create and extract archive files. Windows Explorer and the macOS Finder can create and expand compressed ZIP files. Unix and Linux can create and expand TAR files with or without gzip compression. Third-party archiving utilities like WinRAR and 7-Zip can create other types of archive files using a variety of compression algorithms. Some archive formats, like RAR, even support splitting an archive into several smaller chunks that can be reassembled later.
NOTE: Common archive file extensions include .ZIP, .TAR, .7Z, .RAR, .TAR.GZ, and .TGZ.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge