NAT
Stands for "Network Address Translation."
NAT is a method of translating multiple internal IP addresses of computers on a local network to a single shared global IP address. Network routers use NAT to direct incoming traffic from the Internet to the correct destination on the local network. In addition to allowing multiple computers to share a single global IP address, NAT improves the security of a network by obscuring the local IP addresses of individual computers from the outside.
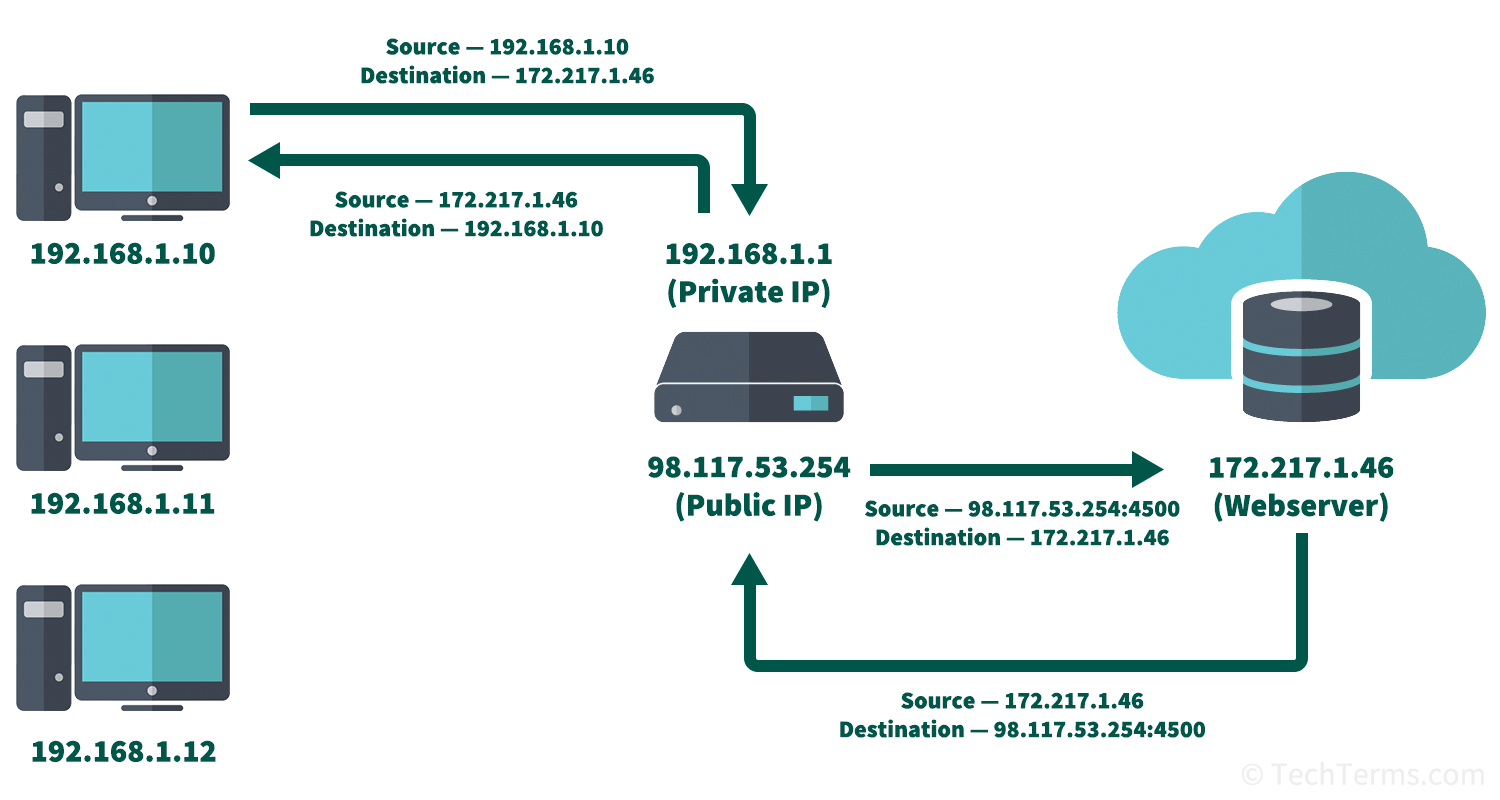
Every device on a LAN has a private IP address for communication within that network. Typically, the only device on a local network with a public and globally-unique IP address is the modem or gateway that provides its connection to the Internet. The network's router uses NAT to translate every outgoing data packet by changing the source IP address from the computer's private address to the gateway's public one. It also replaces the source's port number with a new unique port number and saves that port to a record in a NAT table. When the router receives incoming data packets, it identifies the destination using the port number. It looks up that port in the NAT table and translates the destination address back to the correct computer's private address.
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, which limits the total available namespace to roughly 4 billion addresses; reserved blocks for private networks take up several million of those. Since this number is insufficient for every Internet-connected device to have a unique address, NAT is necessary to provide networked computers with an Internet connection. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, which provides enough address space for several quadrillion unique devices but is not yet universally adopted.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge