Flash Memory
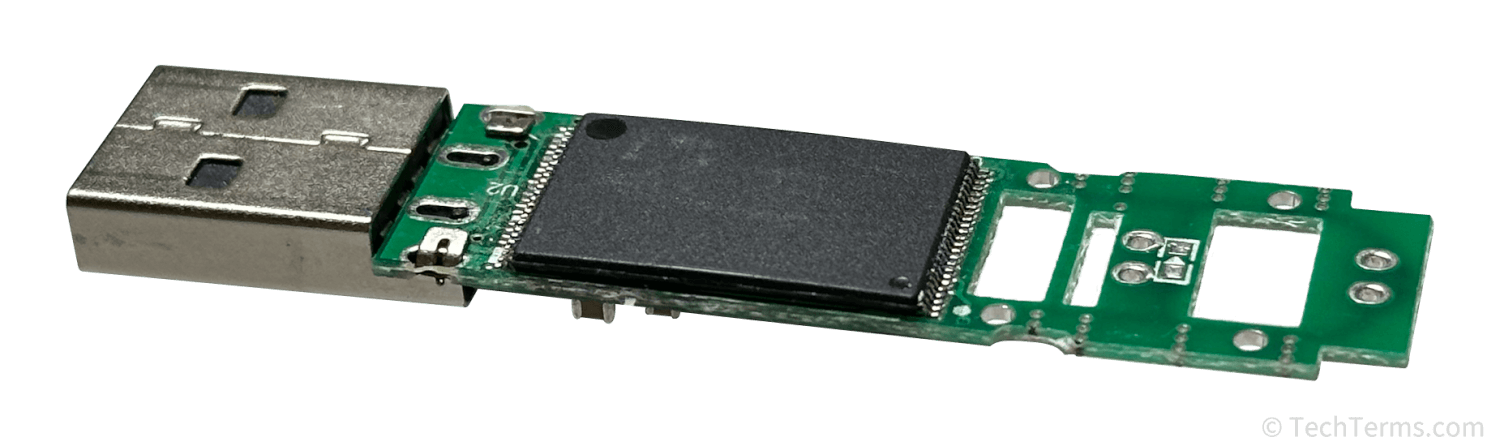
Flash memory is a form of computer ROM chip used in computers, mobile devices, digital cameras, and many other electronic devices. It is non-volatile (preserving data even when powered off) and solid-state (with no moving parts). Flash memory stores firmware instructions for all sorts of electronic devices — computers and smartphones, networking equipment, cars, televisions, and even household appliances. It is also used for general data storage in SSDs, flash drives, SD cards, and embedded disks in mobile devices.
Flash memory is a type of electrically-erasable programmable read-only memory or EEPROM. The name comes from how the memory erases data, clearing a section of memory cells in a single action or "flash." Flash memory was first used for small ROM chips to store a computer's BIOS settings and other firmware data, where the ability to update itself when necessary was valuable.
Over time, the cost of flash memory decreased while storage capacities increased. Cheap flash memory enabled the creation of small memory cards like SD and Compact Flash, as well as small USB flash drives. It is also used in solid-state drives for computers, which can read and write data significantly faster than older hard disk drives that rely on spinning platters. Since flash memory is compact and has no moving parts, it is also ideal for storing data on laptop computers, smartphones, and tablets.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge