Buffer
A buffer is a temporary, intermediate storage area in a computer's memory that holds data while it transfers between two locations. These locations may be physical (for example, separate computers on a network or hardware components inside a computer) or virtual (two programs running on one computer). A buffer smooths out a data transfer when one side has a slower connection or less processing ability than the other side. It allows some data to build up in memory to provide the receiving end with a steady data flow, even if the sending end experiences fluctuations or interruptions.
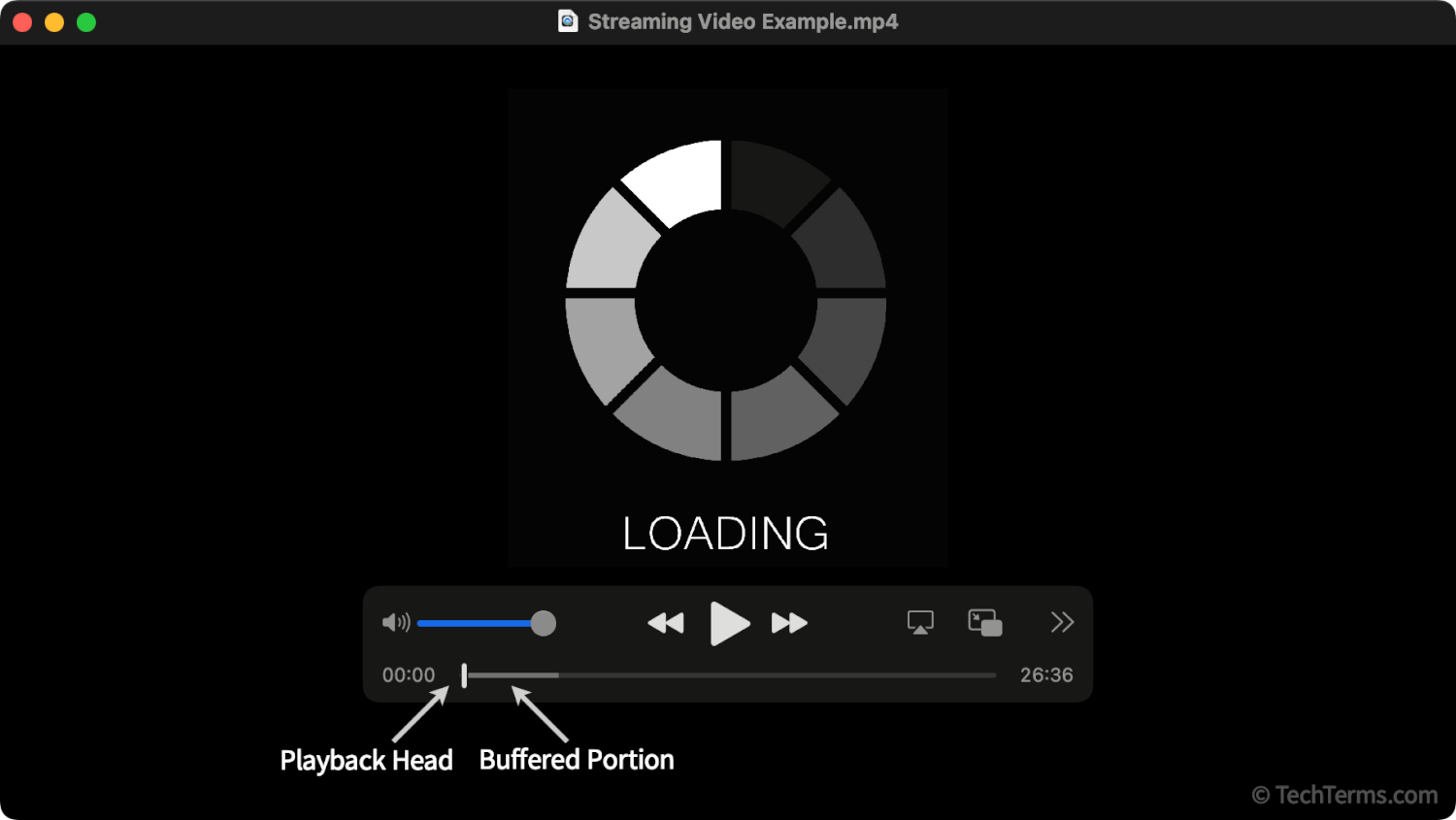
The most visible example of a buffer most computer users see is when a streaming video downloads for a few seconds before it starts playing. Buffering the video allows the computer playing the video to play it back without pausing, even if the connection is not fast or consistent enough to play it directly over the Internet. If the connection drops entirely, the video still plays back until it reaches the end of the buffer (or the end of the video if the computer managed to buffer the entire thing).
Many other aspects of computers use buffers to help manage data transfers, using part of the system RAM or some dedicated memory on a hardware component. For example, hard drives include a built-in memory buffer to store data during read-and-write operations, since hard drives cannot write data as fast as the storage controller sends it. Video cards render 2D and 3D graphics to a frame buffer before sending the resulting images to the monitor to keep the video frame rate smooth. Even mouse clicks and keystrokes first go to a memory buffer for a moment before the operating system processes them as input.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge