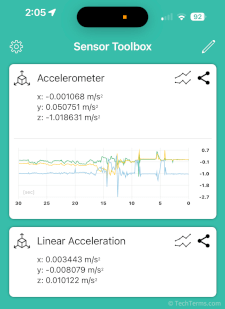
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a sensor that measures vibration or acceleration forces on an object. An accelerometer can detect both static forces, like gravity, and dynamic forces, like vibrations and changes in acceleration and direction. Small accelerometers are integrated into smartphones, fitness trackers, game controllers, and other electronic devices to help them to detect movement and orientation.
The most common type of accelerometer used in electronic devices is a capacitive accelerometer. This type of sensor includes a small mass connected to springs (or other flexible supports) and suspended between fixed capacitive plates. As the device moves, this small mass moves on its springs. This movement changes the distance between the fixed plates and the mass, resulting in a measurable change in electrical energy. The accelerometer converts this change into motion data, including the direction and magnitude of acceleration.
Many different kinds of electronic devices integrate accelerometers for motion tracking. For example, smartphones use them to know when to rotate the screen and for other forms of motion control. Cars and trucks include accelerometers to detect a rapid deceleration resulting from a crash to deploy airbags and other safety features. Airplanes use accelerometers paired with gyroscopes to measure and maintain orientation and help with navigation. Smartwatches and fitness trackers use them to count steps taken and distance traveled during workouts. Finally, game controllers can use accelerometers for motion control in gaming, first popularized with the Nintendo Wii.
NOTE: Accelerometers are one of many kinds of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) found in a smartphone. Other MEMS sensors include gyroscopes, proximity sensors, barometers, compasses, and ambient light sensors.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge