Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents you from using your computer or accessing certain files unless you pay a ransom. It often encrypts your files so that they cannot be opened. Examples of ransomware include Locky, Reveton, CryptoLocker, and CryptoWall.
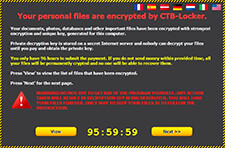
Ransomware is often distributed as a trojan, or malware disguised as a legitimate file. Once installed, it may lock your computer and display a "lockscreen" with a message saying you must pay a ransom to regain use of your computer. This may be a fake message purporting to be from a government institution like the FBI or Department of Defense saying you must pay a fine. It may also be a blatant ransom message saying your files are being held for ransom and you must pay to access them again. The ransom message typically includes instructions for how to pay the fine, often by credit card or Bitcoin. Ransom amounts range from less than $100 to several thousand dollars.
Some ransomware may allow you to use your computer, but will prevent you from opening certain files. When you try to open a file or directory encrypted by the ransomware, you may see a message or alert box stating your files are being held for ransom and you must pay a fee to regain access to them.
Dealing with Ransomware
The best way to deal with ransomware is to prevent it. Don't open unknown files or downloads from untrusted websites. You may also want to install antivirus or Internet security software that can detect and eliminate ransomware threats before they take over your computer. This is especially true if you use Windows, as it is the platform most commonly targeted by ransomware.
If your computer is infected with ransomware, you have a few options.
- If you have a recent system backup, you can revert to a saved state before the ransomware infected your computer.
- Search for an Internet security utility that can remove the specific ransomware installed on your system and possibly decrypt your files.
- (Not recommended) Pay the ransomware fee and contact your bank or credit card company to block or refund the transaction.
NOTE: TechTerms does not recommend paying a ransom to remove ransomware. There is no guarantee that paying the fee will remove the ransomware for your computer. The best way to recover from a ransomware attack is to restore your files from a recent backup.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge